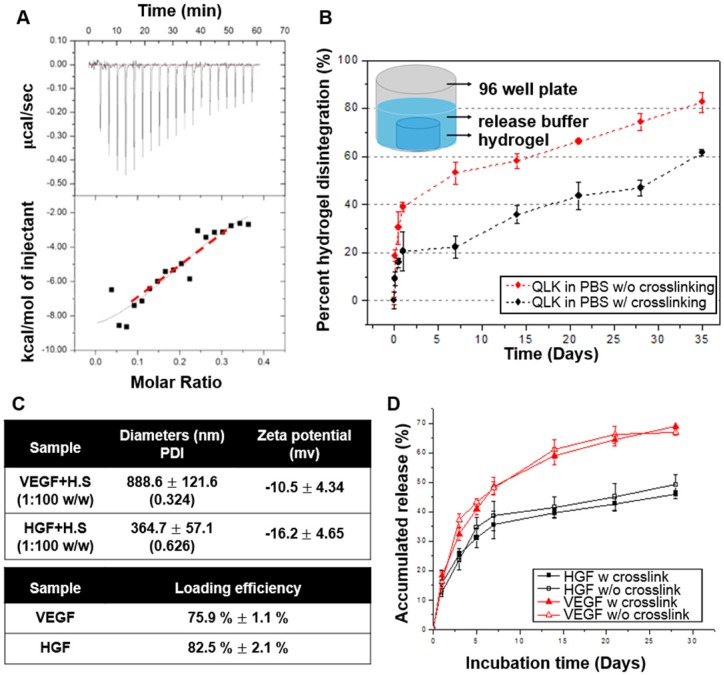
Figure 4.
(A) Isothermal titration calorimetry evaluated the binding of HS to LRK peptide solution. The top graph indicated the heat released upon the addition of HS into LRK solution, and the bottom graph showed the integrated values (black squares) and the fitting line (red line) (binding constant Ka =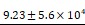 M-1). (B) Disintegration profile of 2 % (w/v) QLK hydrogel without mTG (red) and after mTG (20 U/mL) crosslinking (black), the crosslinking process delayed the dissociation rate of hydrogel scaffold. (C) The diameters, surface charges of the complexes of HS and VEGF, HGF respectively; the GFs loading efficiency were analyzed by ELISA kits. (D) In vitro cumulative release profiles of VEGF and HGF from GAG-assisted self-assembling QLK/LRK peptide hydrogel with or without mTG crosslinking. HGF (black) and VEGF (red) were released from peptide hydrogel scaffold in a sustained fashion for 28 days. Error bars indicated mean ± S.D. for total n = 6.
M-1). (B) Disintegration profile of 2 % (w/v) QLK hydrogel without mTG (red) and after mTG (20 U/mL) crosslinking (black), the crosslinking process delayed the dissociation rate of hydrogel scaffold. (C) The diameters, surface charges of the complexes of HS and VEGF, HGF respectively; the GFs loading efficiency were analyzed by ELISA kits. (D) In vitro cumulative release profiles of VEGF and HGF from GAG-assisted self-assembling QLK/LRK peptide hydrogel with or without mTG crosslinking. HGF (black) and VEGF (red) were released from peptide hydrogel scaffold in a sustained fashion for 28 days. Error bars indicated mean ± S.D. for total n = 6.