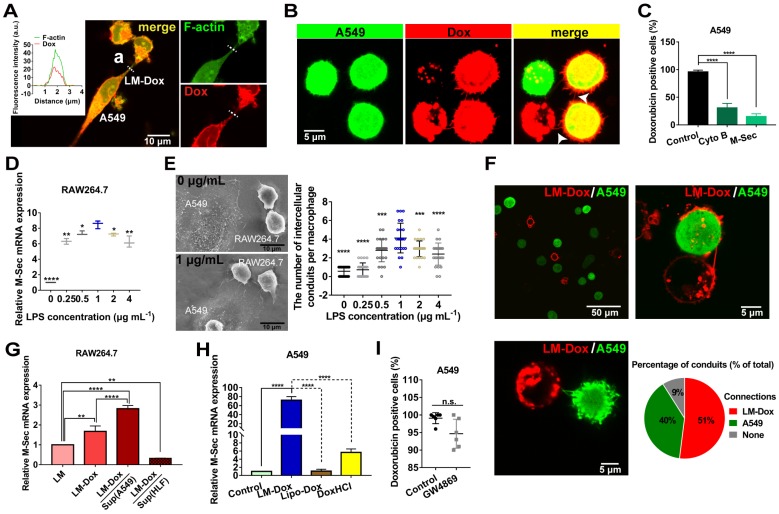
Figure 2.
LM-Dox stimulated intercellular conduit formation and hijacked tumor microtube networks of tumor cells for enhancement of drug transfer. (A) Transport of Dox between intercellular conduit-connected LM-Dox and A549 cells. F-actin, the vital component of these membrane conduits was stained with phalloidin (green), and Dox emitted red intrinsic fluorescence. (a) Plot profile of the representative images of fluorescence co-localization of the intercellular conduit and Dox. (B) Images of Dox delivery from LM-Dox to A549 cells via intercellular conduits. Intercellular conduits are indicated by white arrows. Scale bar, 5 μm. (C) The Dox positive A549 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. The A549 cells were pretreated with CytoB and M-Sec siRNA before incubated with LM-Dox (n = 3). (D) Relative quantification of M-Sec mRNA expression in RAW264.7 using real-time qPCR. (E) Quantification of the number of intercellular conduits extended from per macrophage and relevant SEM images of macrophages with LPS modification. Scale bars, 10 µm. (F) Representative CLSM images of intercellular conduits between LM-Dox and A549 cells and the percentage of intercellular conduits protruded from LM-Dox and A549 cells (n = 50). (G) Relative quantification of M-Sec mRNA expression in LM, LM-Dox and LM-Dox stimulated by the supernatants of A549 or HLF cell culture. (H) Real-time qPCR assay for M-Sec mRNA detection of A549 cells with the treatment of LM-Dox, Lipo-Dox and DoxHCl. A549 cells were incubated with LM-Dox, M-Dox, Lipo-Dox and DoxHCl (equivalent to 4 μM of Dox) prior to further measurements. (I) The Dox positive A549 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. The A549 cells were pretreated with GW4869 before incubated with LM-Dox (n = 6). The data are shown as mean ± s.d., * is p < 0.05, ** is p < 0.01, *** is p < 0.001, **** is p < 0.0001, by one-way ANOVA test.