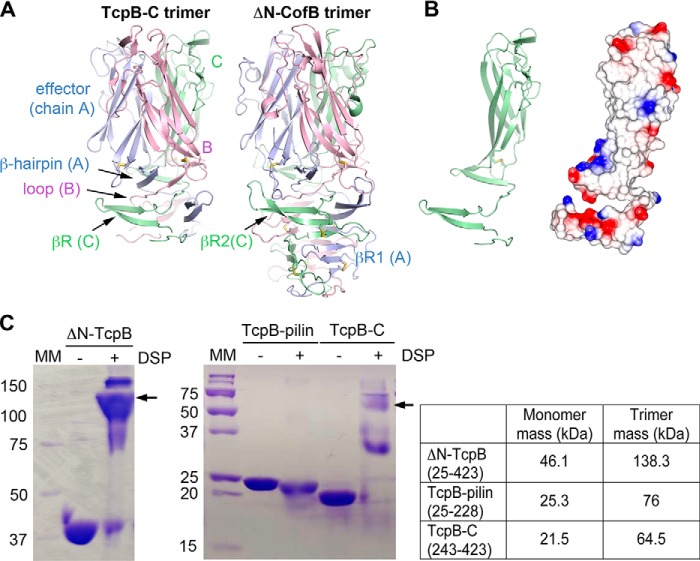
Figure 2.
TcpB-C forms a homotrimer. A, TcpB-C and ΔN-CofB crystallographic trimers, with each subunit, A, B, and C, colored differently. Only the β-repeats and effector domains of the ΔN-CofB structure are shown. B, chain C of TcpB-C, shown in the same orientation as in A, at left in cartoon representation and at right with electrostatic surface potential, calculated using DelPhi (54). Red represents negative charge, blue is positive charge, and white is neutral (scale from −5 to +5 kT). The trimerization surface is mostly uncharged. C, Coomassie-stained nonreducing SDS-PAGE of recombinant TcpB forms in the absence and presence of cross-linker DSP. Fragments containing the C-terminal half of TcpB (residues 243–423) appear at approximately triple their mass in the presence of DSP, indicating the presence of trimers, whereas the TcpB fragment comprising the pilin domain remains as a monomer. The theoretical masses of monomeric and trimeric forms are shown in the table on the right. MM, mass markers (kDa).