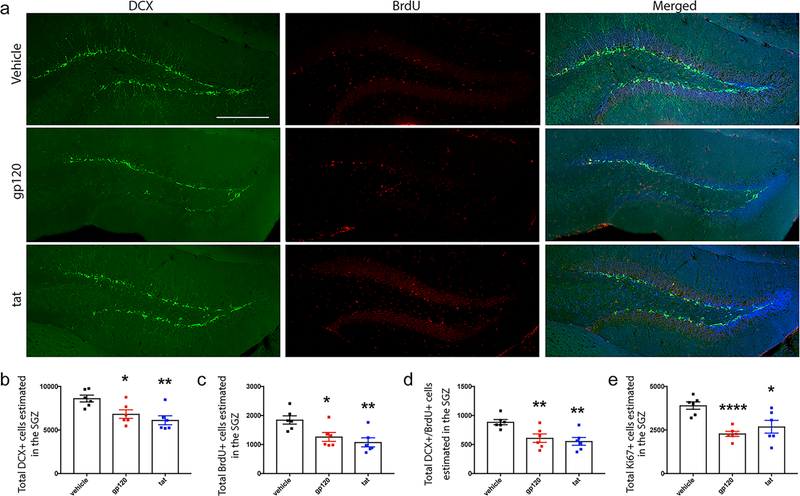
Fig 1. Direct intrahippocampal infusion of HIV-1 neurotoxic proteins gp120 or tat reduces hippocampal neurogenesis in vivo.
Osmotic mini-pumps (Alzet) were implanted sub-dermally into C57BL/6 mice for a continuous dispersion time of 14 days. Pumps contained either vehicle, recombinant gp120 (36 ng/day), or recombinant tat (18 ng/day) and each pump was connected to a stainless-steel cannula which was implanted into the left hippocampus. (a) Representative images depicting the dentate gyrus from 30 μm brain sections of 14-week-old C57BL/6 mice immunostained with anti-BrdU (red) and anti-DCX antibodies (green). Scale bar = 250 μm. Quantitative analysis of DCX (b), BrdU (c), DCX/BrdU (d), and Ki67 (e) total estimated positive cells within the left hippocampus per mouse is shown. Bars represent mean ±SEM, n=6 mice per group. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ****, p<0.0001 as compared to C57BL/6 vehicle group by students T-test.