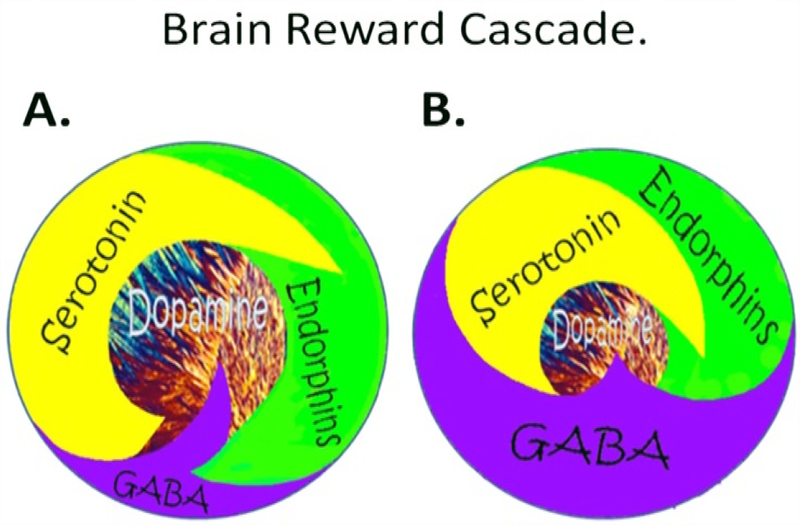
Figure 2.
Schematic of the brain reward cascade: normal and abnormal representation. A The normal physiologic homeostatic state of the neurotransmitter interaction at the mesolimbic region of the brain. In essence, serotonin in the hypothalamus stimulates neuronal projections of methionine enkephalin in the hypothalamus that, in turn, inhibits the release of GABA in the substantia nigra. This allows for the typical amount of dopamine to be released at the nucleus accumbens (NAc) reward site of the brain. B Hypodopaminergic function of the mesolimbic region of the brain. The hypodopaminergic state is due to gene polymorphisms as well as environmental elements (epigenetics), including both stress and neurotoxicity from aberrant abuse of psychoactive drugs (i.e., alcohol, heroin, cocaine, etc.) and genetic variables [with Permission from Blum K]