Figure 3.
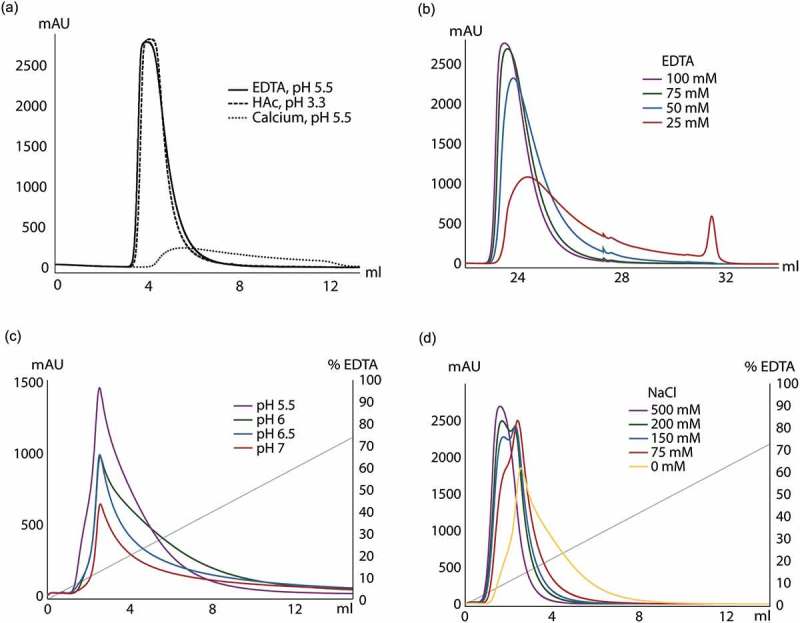
Investigation of elution buffer composition for elution of human polyclonal IgG on a ZCaTetraCys column. (a) IgG was eluted using three different elution buffers: 0.3 M HAc at pH 3.3, 100 mM EDTA at pH 5.5 and 1 mM CaCl2 at pH 5.5. Elution with EDTA at pH 5.5 (solid) gives a very similar elution peak as acidic elution with HAc (dashed), whereas almost no antibody could be eluted at pH 5.5 with calcium present (dotted). (b) Elution using different concentrations of EDTA at pH 5.5 are overlaid: 25 mM (red), 50 mM (blue), 75 mM (green) and 100 mM (purple). Lowering the EDTA concentration to 50 mM or less significantly altered the elution profile. (c) Overlay of gradient elutions between 0–200 mM EDTA at different pH (5.5 in purple, 6 in green, 6.5 in blue and 7 in red) with the gradient profile in gray. This data clearly shows that pH 5.5 renders a more favorable elution profile while also giving the largest amount of product. (d) Gradient elution using 0–200 mM EDTA (gray) at different sodium chloride concentrations: 75 mM (red), 150 mM (blue), 200 mM (green) and 500 mM (purple). The addition of sodium chloride to the elution buffer leads to elution at lower EDTA concentrations as well as more concentrated elution peaks compared to elution with only EDTA (yellow).
