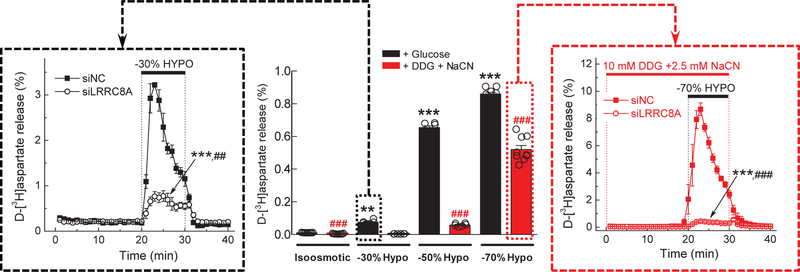
Fig 6. Dramatic cell swelling overrides the metabolic block of VRAC activity.
(central panel) Effects of complete metabolic inhibition on d-[3H]aspartate release in astrocytes exposed to isosmotic medium or various degrees of hypoosmolarity (−30%,−50%, or −70%). Cells were incubated in control glucose-containing media (black bars), or glucose-free media supplemented with 10 mM DDG and 2.5 mM NaCN (red bars). The results are the mean 10-min integral release values ±SEM of 6 experiments per group performed in two different astrocytic cultures. **p <0.01, ***p <0.001, vs isosmotic conditions. ###p < 0.001, metabolically competent vs. metabolically inhibited cells in media with the same osmolarity. (left inset) Molecular biology evidence for VRAC involvement in glutamate release from cells exposed to moderate swelling (−30%). Astrocytes were transfected with negative control siRNA (siNC) or the siRNA targeting the essential VRAC subunit LRRC8A (siLRRC8A). Data are the mean values ±SEM of 3 independent transfections in two different astrocytic cultures. ***p < 0.001, maximal release values vs. siNC. ##p<0.01, integral release values, vs. siNC. (right inset) Molecular biology evidence for VRAC involvement in glutamate release from metabolically inhibited cells exposed to dramatic cell swelling (70% reduction in medium osmolarity). Astrocytes were transfected with siNC or siLRRC8A. Composition of the hypoosmotic media and concentrations of metabolic inhibitors were the same as in central panel. Data are the mean values ±SEM of 4–6 experiments per group performed in two different astrocytic cultures. ***p<0.001, maximal release values vs. siNC. ###p<0.001 integral release values vs. siNC.