Figure 1.
Neuroradiologic and Facial Features of Individuals with De Novo CDH2 Variants
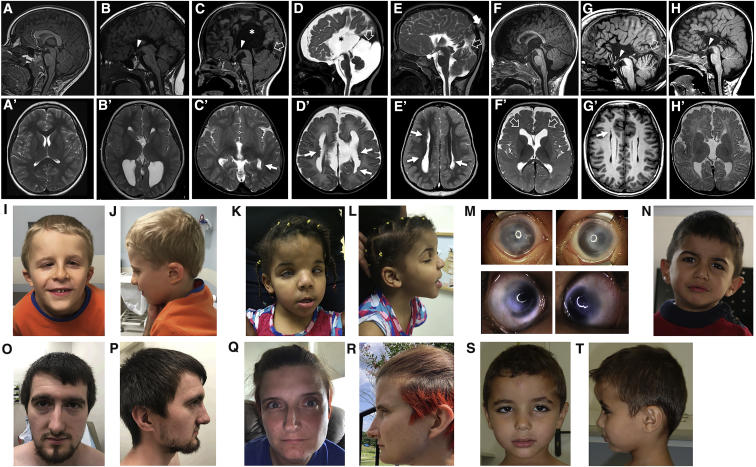
Brain MRI, sagittal T1-weighted (A) and axial T2-weighted (A′) images of a normal subject. Brain MRIs from subject 1 at 7 years (B and B′), subject 2 at 2 years (C and C′), subject 3 at 13 days (D and D′), subject 4 at 4 years (E and E′), subject 5 at 6 months (F and F′), subject 8 at 26 years (G and G′), and subject 9 at 5 months (H and H′) show complete agenesis (B, C, D, E, G, and H) or mild hypoplasia (F) of the corpus callosum; there is an interhemispheric cyst communicating with the III ventricle in two subjects (asterisks in [B] and [D]). In addition, there is hypo-dysplasia of the tentorium in four cases (C, D, E, and G, empty arrows) associated with an atretic parietal cephalocele in one subject (E, arrow). Note the hypothalamic adhesion in subjects 1, 2, 4, 8 and 9 (B, C, E, G, and H, arrowheads), as well as the megacisterna magna in subjects 3 and 8 (D and G). Axial T2 images reveal multiple nodular periventricular heterotopias in four subjects (C′, D′, E′, and G′, arrows), and mild frontal ventriculomegaly in one subject (F′, empty arrows). Photographs of subjects 2 (I and J) and 4 (K and L) demonstrate prominent forehead and frontal bossing, downslanting palpebral fissures, a thin upper lip, and low-set and thick helices. Subject 4 (M) also has Peters anomaly with clouding of the cornea, as well as hypertelorism and epicanthal folds. Subjects 5 (N) and 9 (S and T) have thick earlobes but other major dysmorphisms. Subjects 7 (O and P) and 8 (Q and R) show common craniofacial features, including deep-set eyes, a thin upper lip, a pointed chin, and slightly low-set and posteriorly rotated ears with attached earlobes.