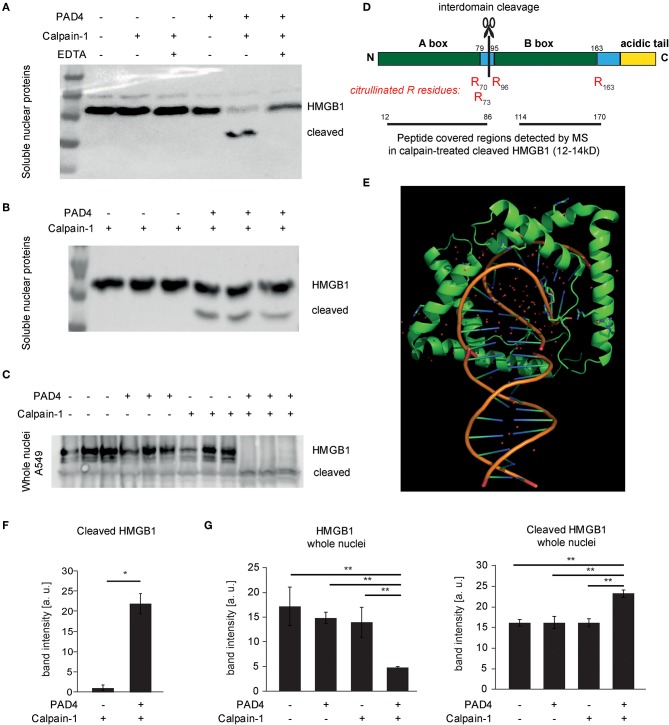
Figure 6.
Cleavage of HMGB1 by calpain and its selective dependence on PAD4. (A,B,F) Soluble nuclear protein lysates of A549 cells were subjected to PAD4-mediated protein citrullination and consecutive calpain-1-mediated proteolysis. HMGB1 was visualized by western blotting using a C-terminal primary anti-HMGB1 antibody (ab18256) (representative of 3 independent experiments). (C,G) Intact isolated A549 nuclei were subjected to enzymatic treatments as in (B) and subjected to western blotting. (D) The molecular organization of HMGB1 is depicted showing the two DNA-binding domains (Box A, Box B) and the acidic tail. Furthermore, the citrullinated arginine residues detected by mass spectrometry (MS) in cleaved HMGB1 (12–14 kD) are depicted in red (R70, R73, R96, R163). Regions covered by peptides identified in the cleaved HMGB1 fragment by MS are highlighted. (E) A structural representation of DNA-binding of two A-boxes of HMGB1 (in green) is depicted showing its binding to kinked DNA (based on PDB: 4QR9) (28). (F) shows respective relative band intensity quantifications of cleaved HMGB1 (student's t-test, *p < 0.05, representative of 3 independent experiments) (G) Intact isolated A549 nuclei were subjected to enzymatic treatments as indicated and subjected to western blotting. Relative band intensity quantifications are presented (ANOVA and post-hoc Tukey HSD, **p < 0.01, representative of 3 independent experiments).