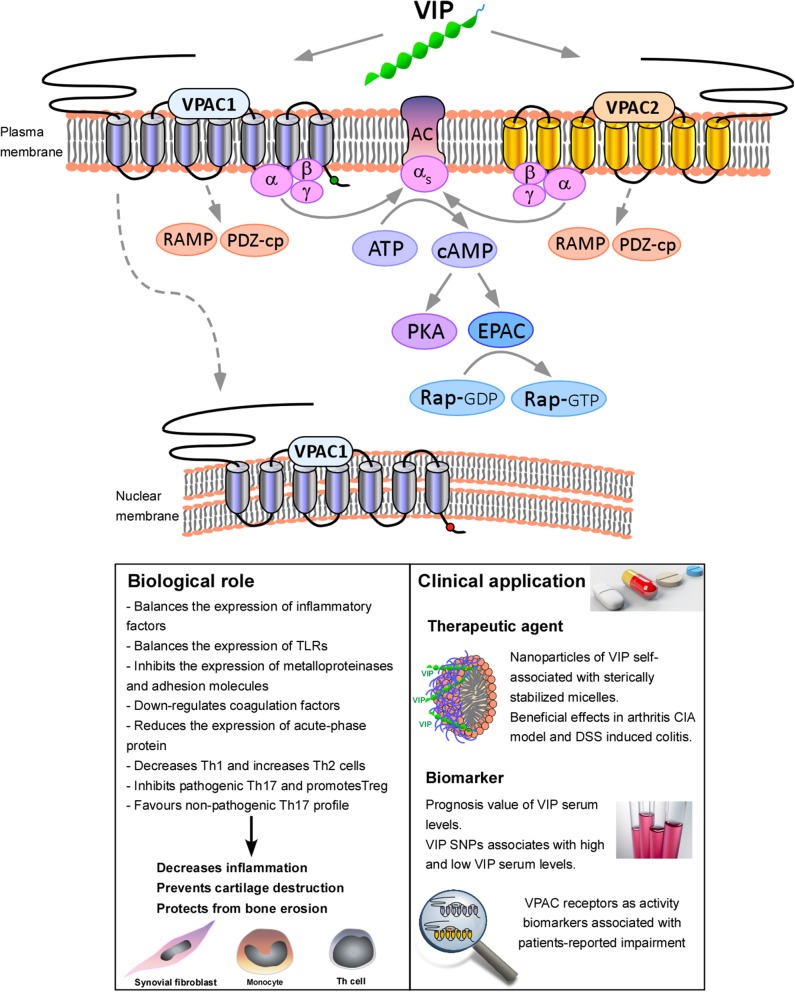
Figure 1.
Functional consequences of VPAC receptors signaling. VIP binds both, VPAC1 and VPAC2. VPAC receptors have greater affinity for Gαs than Gαq, indicating that VPAC receptors preferentially stimulate adenylyl cyclase (AC) activity, increasing cAMP levels and triggering downstream pathways, mainly the canonical PKA pathway and the non-canonical cAMP-activated guanine nucleotide exchange factor (EPAC) pathway. Moreover, these receptors can also interact with accessory GPCR interacting proteins (GIPs), such as RAMPs or PDZ-containing proteins (PDZ-cp). In addition, VPAC1 is also able to translocate to nucleus. Activation of VPAC receptors signaling modulates a number of biological processes, which eventually lead to the decrease of the inflammation, cartilage destruction and bone erosion. In relation to the clinical application, it has been reported the beneficial effects of nanoparticles of VIP self-associated with sterically stabilized micelles (SSMs) in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) murine model (18, 19) and DSS induced colitis (20). We have also demonstrated the prognosis value of VIP serum levels and VIP genetic variants. Moreover, VPAC receptors expression has been described as activity biomarkers associated with patients-reported impairment (21–23).