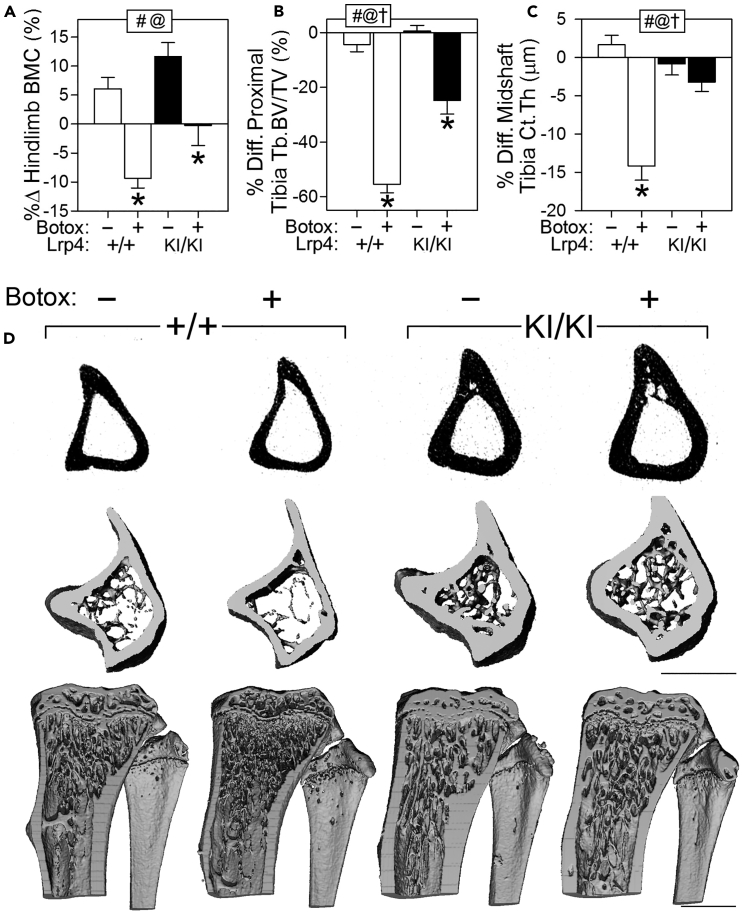
Figure 6.
Lrp4KI Mice Are Partially Protected From Disuse-Induced Bone Loss
(A) Percent change in hindlimb bone mineral density (BMC) following 4 weeks of Botox-induced disuse.
(B and C) Percent difference (from contralateral limb) in trabecular bone volume fraction (Tb.BV/TV) in the proximal tibia and cortical thickness (Ct.Th) in the mid-diaphyseal tibia were significantly greater in Botox-treated WT mice compared with Botox-treated Lrp4KI mice.
(D) μCT reconstructions at the proximal tibia from representative +/+ and KI/KI mice treated with Botox (+) or vehicle (−). Scale bars, 1 mm. Data were tested using two-way ANOVA using Lrp4 genotype and Botox injection as main effects. Inset at the top of each graph indicates significance of the main effects and interaction (# = Lrp4 genotype p < 0.05; @ = Botox effect p < 0.05; † = interaction p < 0.05). When at least one term was significant, Fisher's PLSD post hoc tests were conducted and are indicated as *p < 0.05. For all panels, n = 9–10/group.
Data are presented as means ±SEM. See also Table S6.