Figure 3.
Increased Synapse Numbers, Altered AMPA/NMDA Ratio, and Impaired Plasticity in Adult Conditional Knockout of Lgl1
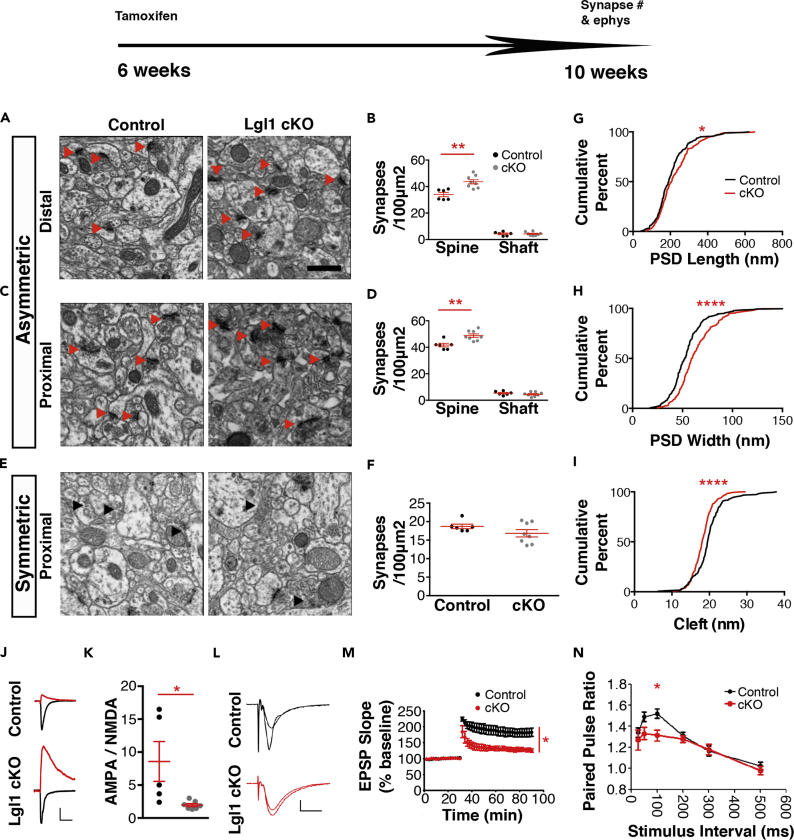
(A) Electron micrographs of the schaffer collateral (SC) 150–200 μm ventral to the CA1 pyramidal cell layer of slices from 10-week-old control and Lgl1 cKO mice following deletion of Lgl1 beginning at 6 weeks of age. Red arrows denote asymmetric synapses. Scale bar, 500 nm. N = 6 control, 8 Lgl1 cKO animals.
(B) Quantification of asymmetric synapse density of the region described in Figure 5A.
(C) Electron micrographs of the SC 50 μm ventral to the CA1 pyramidal cell layer in 10-week-old animals.
(D) Quantification of asymmetric synapses in the proximal region.
(E) Micrographs showing symmetric synapses (black arrows) in the proximal region of the SC.
(F) Quantification of symmetric synapses.
(G) Quantification of cumulative frequency for postsynaptic density (PSD) length.
(H) Quantification for PSD width.
(I) Quantification of synaptic cleft distance. n = 180 Lgl1 control synapses, 242 Lgl1 cKO synapses.
(J) Representative traces of NMDAR current and combined AMPAR/NMDAR current from acute slices taken from 6-week-old control and Lgl1 cKO mice following Lgl1 deletion beginning at P28. Scale bar, 50 pA, 80 ms.
(K) Quantification of the calculated ratio of AMPAR to NMDAR current. N = 5 control, 7 Lgl1 cKO neurons.
(L) Representative traces of EPSPs before and after TBS stimulation was delivered to acute slices from control and Lgl1 cKO mice. Scale bar, 0.2 mV, 10 ms.
(M) Quantification of EPSP slope before and after theta burst stimulation (TBS). N = 5 Lgl1 control, 4 Lgl1 cKO.
(N) Quantification of paired-pulse ratio from control and Lgl1 cKO animals deleted at 6 weeks. N = 6 Lgl1 control, 6 Lgl1 cKO.
*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001.