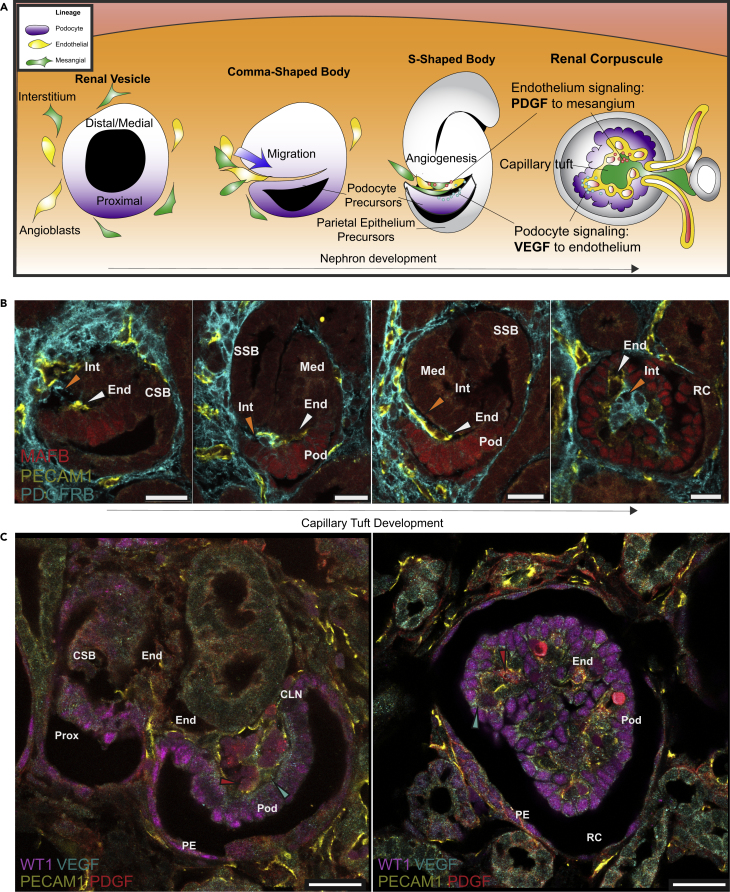
Figure 1.
Schematic Model of RC Development
(A) Differentiating NPCs epithelialize to form a renal vesicle with distal/proximal polarity. Nephron morphogenesis progresses through CSB and SSB stages concomitant with the recruitment and invasion of mesenchymal endothelial and interstitial cells to the glomerular cleft, which is lined by developing podocytes. Podocyte-derived VEGFA signaling to glomerular endothelial cells and PDGF secreted by endothelial cells acting on adjacent mesangial precursors are critical for the development, maintenance, and function of glomerular filtration.
(B) Immunostaining showing incremental stages of glomerular capillary tuft development starting with invasion of PECAM1+ endothelial cells (yellow) followed by PDGFRB + interstitial cells (cyan) into the glomerular cleft (left to right panels).
(C) Immunohistochemical staining of distinct stages of RC development labeling WT1+ PE, WT1+ podocytes colocalized with VEGFA (cyan arrowhead), and PECAM1+ endothelium colocalized with PDGF (red arrowhead).
(Scale bars, 25 μm). Prox, Proximal Nephron; Pod, Podocytes; PE, Parietal Epithelium; End, Endothelium; CSB, Comma-Shaped Body; CLN, Capillary Loop Nephron; RC, Renal Corpuscle.