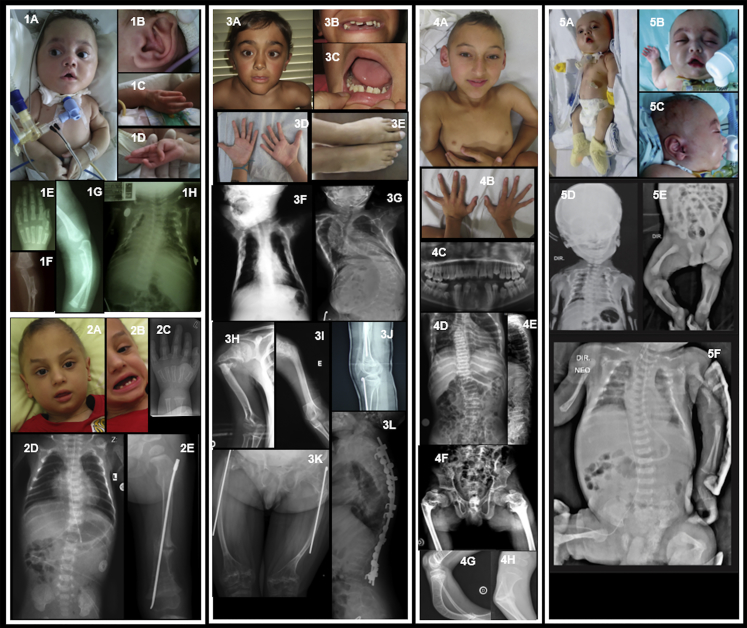
Figure 1.
Clinical and Radiological Features of Individuals with MESD Mutations
(1) Individual 1 from Brazil (Family 1 IV-5)
(1A–1B) Facial dysmorphic features include bluish sclerae, mid-face hypoplasia, arched eyebrows, tented upper lip; also note tracheostomy, narrow chest, and rhizomelia; posteriorly rotated ears.
(1C–1D) Long fingers with adducted thumbs and contractures of the fifth digits.
(1E) Radiograph of left hand showing long, tapering fingers.
(1F–1G) Fracture of left ulna and radius at 5 months, healing with callus formation.
(1H) Radiograph of chest at 5 months showing bell-shaped, narrow chest with multiple (healing) rib fractures.
(2) Individual 2 from Turkey (Family 2 IV-1)
(2A–2B) Facial dysmorphic features include tall forehead, arched eyebrows with sparse lateral thirds, micrognathia, posteriorly rotated ears, widely spaced teeth, and oligodontia.
(2C) Radiograph of left hand at 8 months showing long, tapering fingers.
(2D) Chest radiograph at 5 months showing bell-shaped thorax, thin ribs with healing posterior rib fractures.
(2E) Fracture of the left femur at age 4 years, post-surgical rodding.
(3) Individual 3 from Portugal (Family 3 V-2)
(3A–3C) Facial dysmorphic features include triangular facies, arched eyebrows, left convergent strabismus, midface hypoplasia, thin upper lip, pointed chin, widely spaced teeth, and oligodontia.
(3D) Hands showing long fingers with mild contractures.
(3E) Feet showing 2-3 partial cutaneous syndactyly with overlapping toes.
(3F–3G) Chest radiographs at 6 months and 12 years, respectively, showing multiple rib fractures and progressive scoliosis with vertebral compression fractures.
(3H–3I) Upper limb radiographs showing right and left humeral fractures, respectively.
(3J) Right knee at age 8 years, showing signs of cyclical pamidronate therapy, rodding of the tibia, and very gracile fibula.
(3K) Aged 16 years, thin femurs with bilateral rodding of the femoral shafts post-fracture.
(3L) Lateral spinal radiographs at 12 years, showing osteopenia, progressive vertebral compression fractures, and spinal fixation.
(4) Individual 4 from Brazil (Family 4 II-2)
(4A) He has minimal facial dysmorphic features, slightly upslanting palpebral fissures, and a pointed chin; sclerae are white; skeletal deformity with rhizomelic shortening is noted.
(4B) Impression of long fingers with mild interphalangeal contractures.
(4C) Panorex radiograph showing disorganized dentition, abnormal premolars, and missing lower jaw teeth (numbers 31, 32, and 41).
(4D–4E) Radiographs showing osteopenia, narrow chest, thin ribs with fractures, scoliosis, and vertebral compression fractures.
(4F–4H) Radiographs showing skeletal deformity and evidence of fractures of the femoral necks and tibiae.
(5) Individual 5 from Brazil (Family 5 IV-1)
(5A–5C) Facial dysmorphic features include round face, prominent eyes with long lashes and epicanthic folds, small nose with bulbous tip, tented upper lip, high and narrow palate, retrognathia, and posteriorly rotated ears; also note narrow thorax with inverted nipples, rhizomelic shortening of limbs, and long fingers with contractures.
(5D–5F) Radiographs showing generalized osteopenia, multiple fractures (clavicles, ribs, left humerus, femur), narrow thorax, and bowing of femurs bilaterally.