Fig. 3.
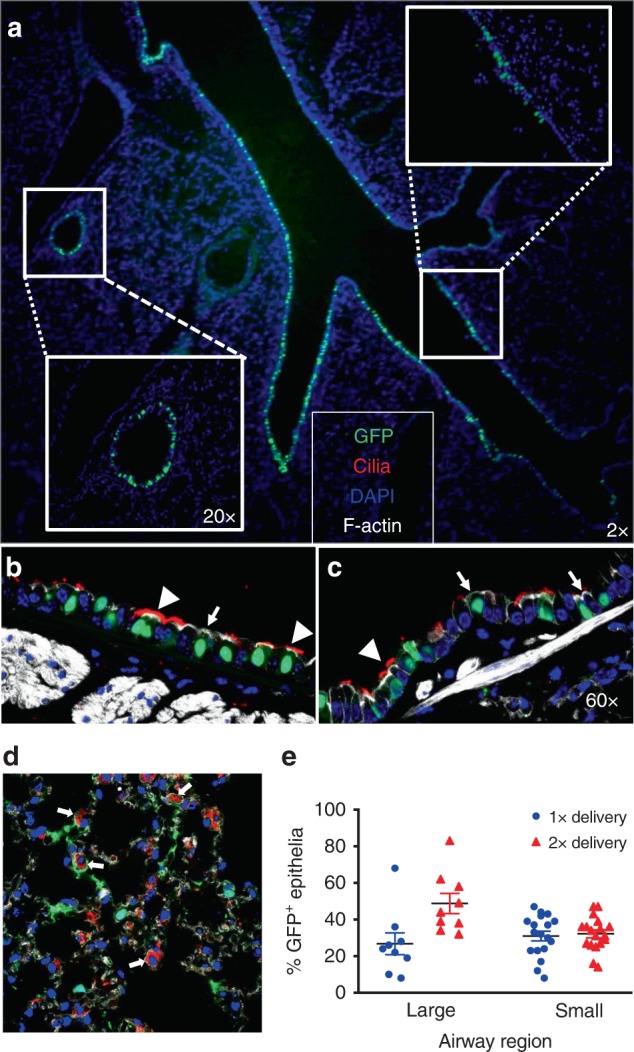
GFP-NLS protein delivery to mouse airways using S10 peptide. a Fluorescence image of lung tissue section 18 h following two intranasal doses of [S10]: 40 µM; [GFP]: 20 µM in 50 μl; ×2 magnification. Insets show the large and small airways at ×20 magnification. b, c Localization of GFP in different cell types. GFP co-localized with specific markers of cilia (α-tubulin, red), F-actin (phalloidin stain, gray), and nuclei (DAPI, blue) in large (b) and small airway epithelia (c). Non-ciliated cells were identified by the absence of α-tubulin staining; ×40 magnification. Arrowheads indicate ciliated cells (α-tubulin); arrows indicate non-ciliated cells. n = 4 mice per group. d GFP localization in distal lung region. Co-localization of GFP and SP-C (red), a marker of alveolar type II cells, F-actin (phalloidin stain, gray), and nuclei (DAPI, blue); ×40 magnification. White arrows indicate co-localization of GFP and SP-C. e Quantitation of GFP+ cells in large and small airways following 1 or 2 deliveries of GFP protein. Results are presented as mean ± SE; n = 4 mice per group. Data underlying this figure are provided as Source Data file
