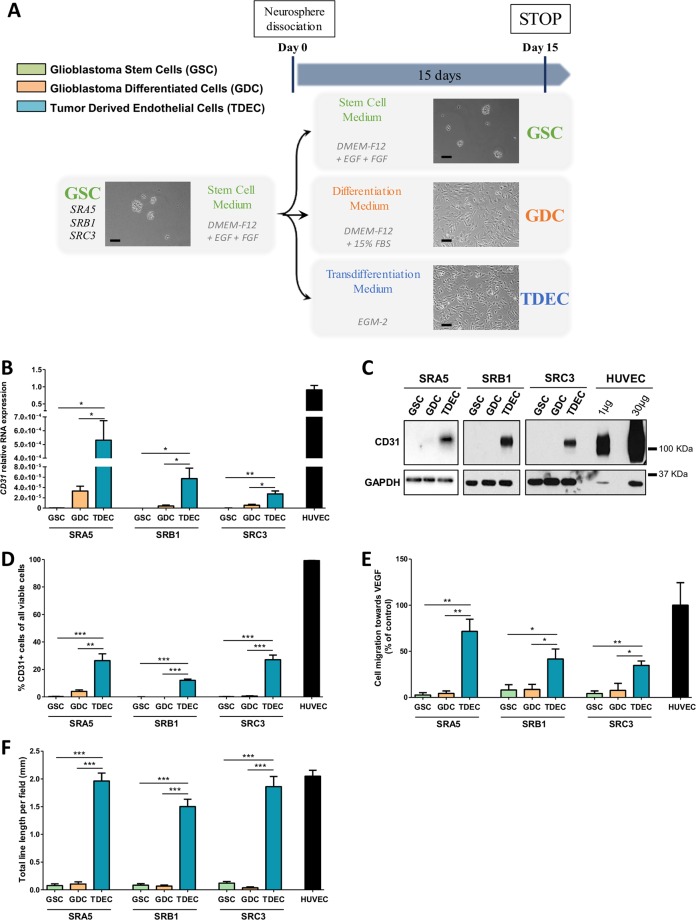
Fig. 1. GSC cultured under conditions of endothelial differentiation develop phenotypical and functional features of endothelial cells.
a Overview of the different cell culture protocols. As described in the Materials and Methods section, GSC-enriched neurospheres were isolated from patient samples and cultured in a specific stem cell medium (DMEM-F12 with EGF (epidermal growth factor) and FGF (fibroblast growth factor) growth factors). Neurospheres were then dissociated and placed for at least 15 days (i) in stem cell medium to keep GSC in culture as a control, (ii) in differentiation medium (DMEM-F12 with 15% FBS (fetal bovine serum) to obtain GDC or (iii) in transdifferentiation medium (EGM-2) to obtain TDEC. Scale bars, 100 µm. b Relative RNA expression of the endothelial marker CD31 determined by RT-qPCR in GSC, GDC, TDEC and HUVEC. Results are normalized to HUVEC expression. c Immunoblot of CD31 in GSC, GDC, TDEC, and HUVEC. Blots are representative of at least 3 independent experiments in the three patients’ GSC lines (SRA5, SRB1, and SRC3). d FACS immunofluorescence analysis of CD31 protein expression in GSC, GDC, TDEC and HUVEC. The graph represents means ± SEM of the percentage of CD31 positive cells among all viable cells of at least 3 independent experiments. e Percentage of cells that migrate towards VEGF normalized to HUVEC. f. Pseudotube formation assay. The graph represents means ± SEM of the total line length per field determined by the quantification of at least 3 fields per well