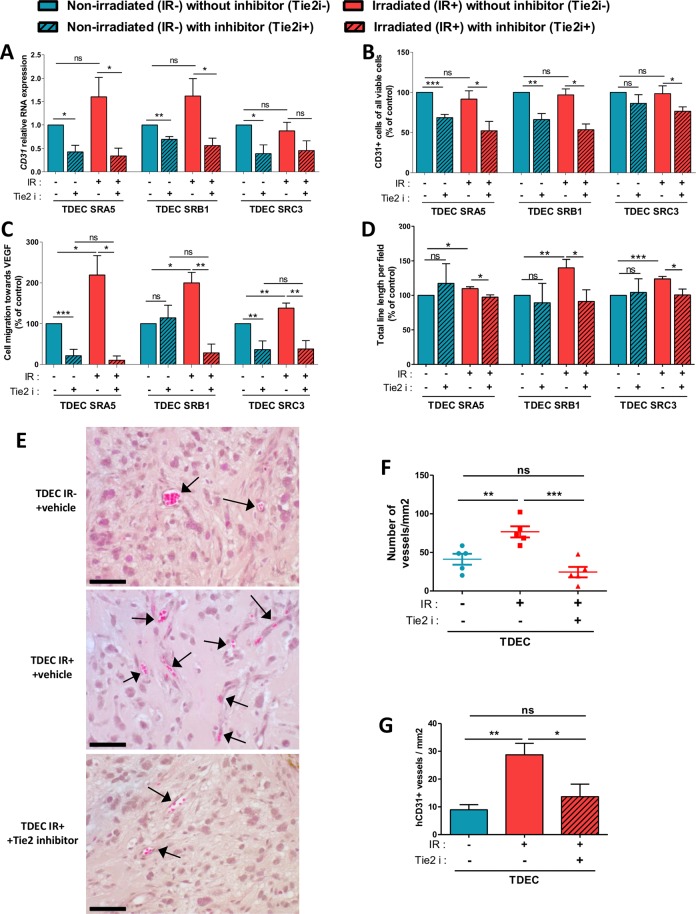
Fig. 5. Tie2 kinase inhibitor (Tie2i) decreases the IR-induced effect on TDEC.
a Relative RNA expression of the endothelial marker CD31 determined by RT-qPCR in TDEC IR− vs. TDEC IR+ from the three different GSC (SRA5, SRB1 and SRC3) and cultured with or without Tie2i. The fold inductions are expressed as means ± SEM of at least three independent experiments (normalized to TDEC IR− obtained from each GSC and cultured without Tie2i). b Flow cytometric analysis of CD31 expression in TDEC IR− and TDEC IR+ obtained from SRA5, SRB1 and SRC3 GSC and cultured with or without Tie2i. The level of CD31 positive cells is expressed as means ± SEM normalized to TDEC IR- obtained from each GSC and cultured without Tie2i. c The percentage of cells that migrate towards VEGF normalized to TDEC IR- obtained from each GSC and cultured without Tie2i. d Pseudotube formation assay. The graph represents means ± SEM of the total line length per field determined by the quantification of at least 3 fields per well normalized to TDEC IR− without Tie2i obtained from each GSC. e MatrigelTM plug assay. Representative hematoxylin-eosin sections of MatrigelTM plugs with TDEC IR− without Tie2i, TDEC IR+ without Tie2i and TDEC IR+ with Tie2i. Black arrows indicate functional blood vessels. Scale bars, 50 µm. f Quantification of functional blood vessels in MatrigelTM plugs/mm2. The number of vessels/mm2 was expressed as means ± SEM of 5 mice for TDEC IR− without Tie2i and TDEC IR+ without Tie2i and of 4 mice for TDEC IR+ with Tie2i. g Quantification of hCD31 + vessels in MatrigelTM plugs/mm2. The number of hCD31 vessels per mm2 was quantified and expressed as means ± SEM of 5 mice for TDEC IR− without Tie2i and TDEC IR+ without Tie2i and of 4 mice for TDEC IR+ with Tie2i