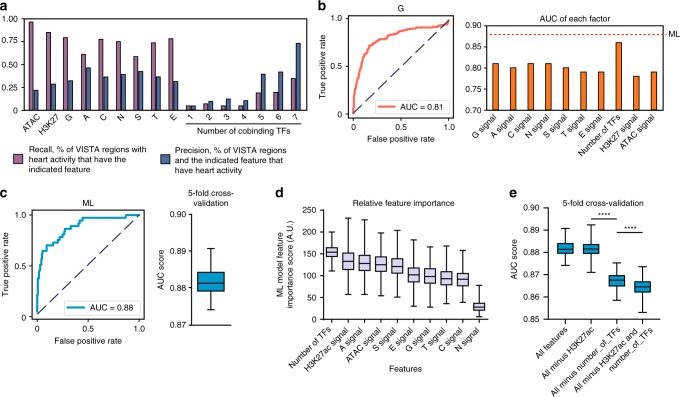
Fig. 5.
Multi-TF co-occupancy contributes to prediction of active heart enhancers. The VISTA enhancer database41 was used as the gold standard to develop classifiers of transcriptional enhancers based on TF co-occupancy, H3K27ac occupancy, and chromatin accessibility. a Recall and precision of VISTA heart enhancer activity based on heart chromatin features. b VISTA heart enhancer receiver-operating characteristic curve and area-under-the-curve (AUC) scores for each factor. An example ROC curve for enhancer prediction by fetal GATA4 bioChIP-signal is shown in the left panel. Similar analyses of other chromatin features is shown in Supplementary Fig. 13. The right plot summarizes the predictive accuracy, assessed by the AUC, for the indicated chromatin features. c Machine learning (ML) classifier performance for classification of VISTA heart enhancers. An ensemble decision tree-based classifier was trained using 80% of the data and tested on the remainder. Classifier performance receiver-operating characteristic curve (left) yielded AUC = 0.88. Performance in 100 permutations of five-fold cross-validation is shown by the box plot to the right. The average ML classifier AUC is indicated by the red dashed line in panel b. d Relative feature importance in the ML classifier. The box plots show the relative importance of individual chromatin features for classifier performance in 100 permutations of five-fold cross validation. e Effect of omission of top ranked classifier features on classifier performance. Omission of H3K27ac signal did not affect classifier performance, but omission of “number of TFs” impaired classifier performance. Box plots in figure; 1st through 3rd quartile represented by box and whiskers denoting min and max values, Source data for panels a-e are provided as a Source Data file