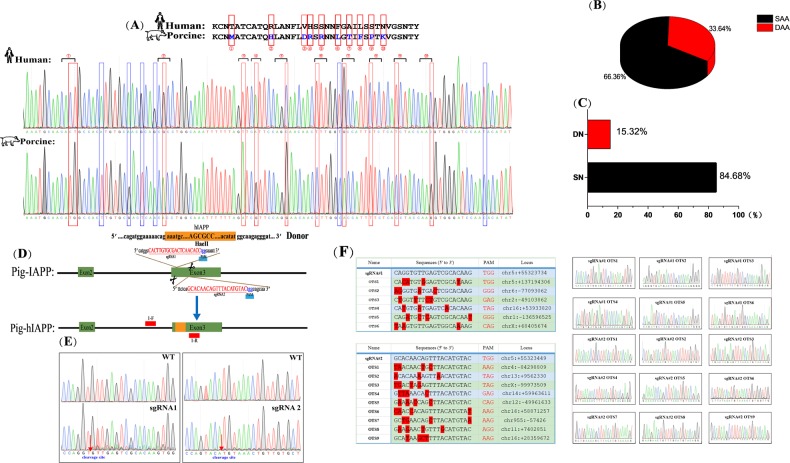
Fig. 2. Sequence analysis of mature pig-to-human IAPP protein and construction of the humanized IAPP gene CRISPR/Cas9 system.
a Sequence homology comparison between pig and human IAPP mature protein. The red box marks the different nucleotide sequences of the porcine and human IAPP mature proteins. The blue box marks the nucleotide sequence that does not cause amino acid changes. b A pie chart of amino acid differences between the pig and human mature IAPP proteins. The red part indicates the percentage of differential amino acids (33.64%); the black part indicates the percentage of the same amino acids. c A nucleotide difference pie chart corresponding to the mature IAPP protein of pigs and humans. The red part indicates the percentage of differential nucleotides (15.32%); the black part indicates the percentage of the same nucleotides (84.68%). d Schematic representation of sgRNAs to porcine IAPP exon 3. sgRNA targeting sequences are shown, and PAMs are highlighted in blue. e Genomic sequences of CRISPR target regions in wild-type PFFs and transfected PFFs, as indicated. Cleavage sites are labeled with red arrows. f Off-target detection. The sequencing peaks showed that both sgRNAs were not cleaved at other sites