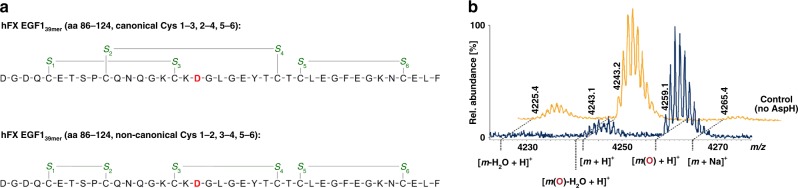
Fig. 5.
AspH fully hydroxylates a mixture of canonical and non-canonical EGFD disulfides under redox conditions. End-point turnover reactions were performed as in the Methods Section. a Schematic structures of the two major hFX EGF139mer disulfide isomers identified in a single batch of hFX EGF139mer obtained by thiol oxidation in air-saturated buffer (see Supplementary Information); disulfides are in green (canonical isomer, Cys1–3, 2–4, 5–6, top; non-canonical isomer, Cys1–2, 3–4, 5–6, bottom), the hydroxylation sites (Asp103hFX) are in red. b >95% Hydroxylation of hFX EGF139mer was observed under redox conditions as opposed to partial hydroxylation under standard (non-redox) conditions (Fig. 1c), indicating that a ‘non-canonical’ EGFD-disulfide pattern (Cys 1–2, 3–4, 5–6) is the actual AspH-substrate; the light orange graph represents a control in which AspH was replaced by buffer