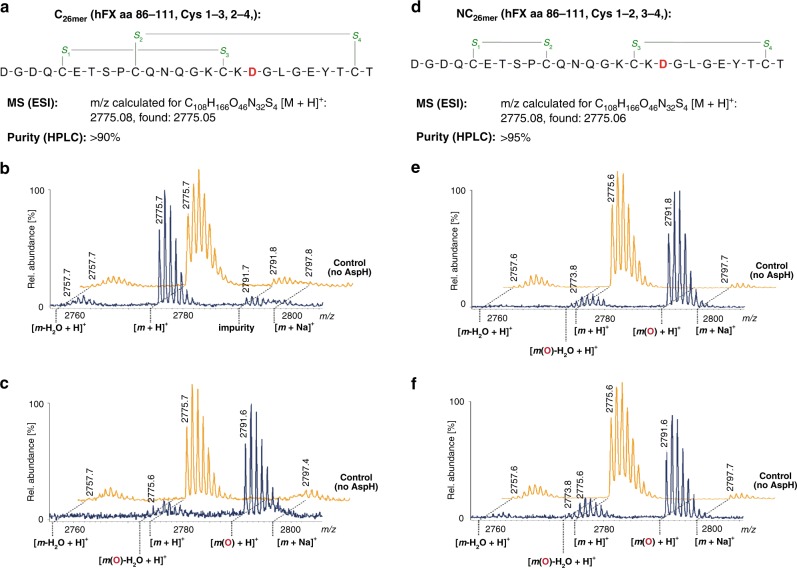
Fig. 7.
The EGFD disulfide connectivity determines the degree of AspH-catalysed hydroxylation under non-redox conditions. End-point turnover reactions were performed as in the Methods Section. Light orange graphs represent controls in which AspH was replaced by buffer. a Schematic structure and calculated mass of the C26mer peptide, bearing a canonical disulfide arrangement (Cys1–3, 2–4); disulfides are shown in green, the hydroxylation site (Asp103hFX) is indicated in red. b No hydroxylation of the C26mer peptide was observed under standard (non-redox) conditions; ~7% impurity (might correspond to an oxidized byproduct) was observed in this sample, including the control samples. c >95% Hydroxylation of the C26mer peptide was observed under redox conditions. d Schematic structure and calculated mass of the NC26mer peptide, bearing a non-canonical disulfide arrangement (Cys1–2, 3–4); disulfides are in green, the hydroxylation site (Asp103hFX) is in red. e >95% Hydroxylation of the NC26mer peptide was observed under standard (non-redox) conditions. f ~83% Hydroxylation of the NC26mer peptide was observed under redox conditions