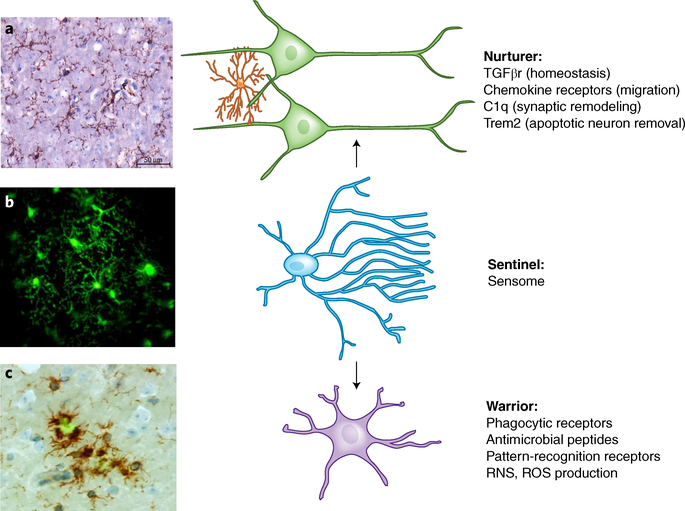
Fig. 2 |. Three proposed functional states of microglia.
a, Nurturer state: microglia (left) stained for Cd11b (brown) in a normal brain are highly ramified and evenly spaced throughout the brain parenchyma. In their nurturer role they maintain milieu homeostasis, participate in synaptic remodeling and migration, and remove apoptotic neurons, all mediated by specific receptors and receptor-linked pathways. b, Sentinel state: micrograph taken from a video using two-photon microscopy from a Cx3cr1-GFP mouse with a cranial window shows a cluster of green microglia with abundant processes. The video from which this micrograph was taken (Supplementary Video 1) shows that microglia (green) processes are in constant motion, surveilling their surroundings. Focal laser-induced injury initiates microglia response, with those microglia closest to the site of injury displaying polarization of surveilling processes toward the area of injury. Microglia sensing is mediated by proteins encoded by sensome genes, which are portals for microglia to perform their housekeeping and host-defense functions. c, Warrior state: microglia (left) stained for Cd11b (brown) accumulate around Aβ deposits stained with thioflavin-S (green), where they are observed to be two- to fivefold denser than in neighboring areas. The warrior morphology becomes stockier and less ramified, and defense against infectious pathogens and injurious-self proteins including Aβ is mediated through microglial Fc receptors, TLRs, viral receptors, and antimicrobial peptides. Sensing is a prerequisite for microglia to perform their housekeeping and host-defense functions.