Figure 1.
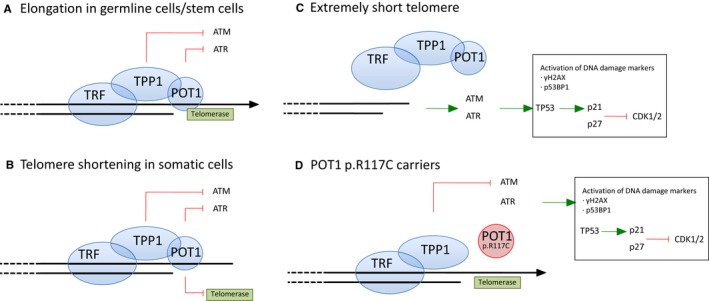
Telomere biology and damage signaling. A, Elongation in germline/stem cells. The shelterin complex mediates telomere elongation by recruiting telomerase. Shelterin also represses the DNA damage response by preventing the activation of ATM and ATR through TPP1 and POT1 proteins, respectively. TPP1 is anchored to the chromosome by POT1 and TRF (telomeric repeat binding factor 1), which is another component of the shelterin complex. B, Telomere shortening in somatic cells. Somatic divisions entail telomere shortening due to the inhibition of telomerase recruitment mediated by the POT1 protein. C, Extremely short telomere. The shelterin complex cannot bind critically short telomeres. DNA damage response ATM/ATR activates the TP53/p21 cascade to inhibit CDK1/2. DNA damage markers such as γH2AX and TP53BP1 bind the short telomeres. DNA damage signaling mediates senescence, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis. D,POT1 p.Arg117Cys (p.R117C) mutation carriers. The POT1 p.R117C mutation prevents POT1 from binding to TPP1 and from forming the OB‐fold to bind single‐strand DNA, which prevents POT1 from repressing ATR signaling. Telomere damage response is activated in POT1 p.R117C mutation carriers.
