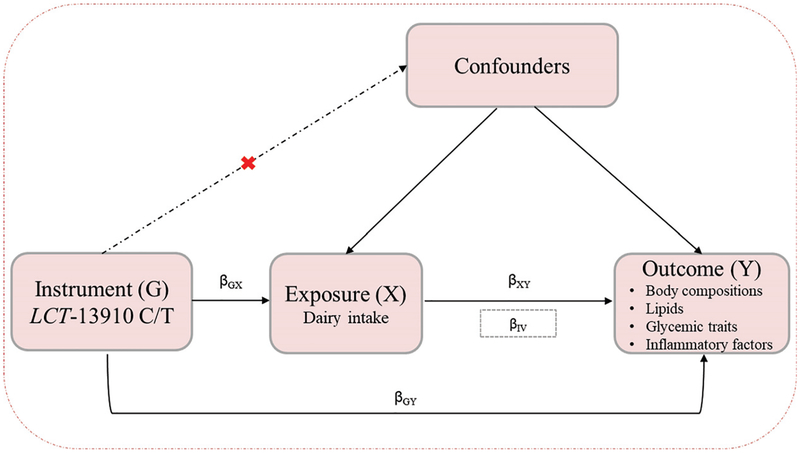
Fig. 1. A schematic description of a Mendelian randomization analysis.
MR can be used to test the hypothesis that exposure (dairy intake) causes outcomes (cardiometabolic traits). Three assumptions of MR: (a) genetic variants must be associated with dairy intake; (b) genetic variants must not be associated with confounders; and (c) genetic variants must influence cardiometabolic traits only through dairy intake, not through other pathways. The IV estimator was used to quantify the strength of the causal association of dairy intake with cardiometabolic traits using LCT-13910 C/T as an IV.