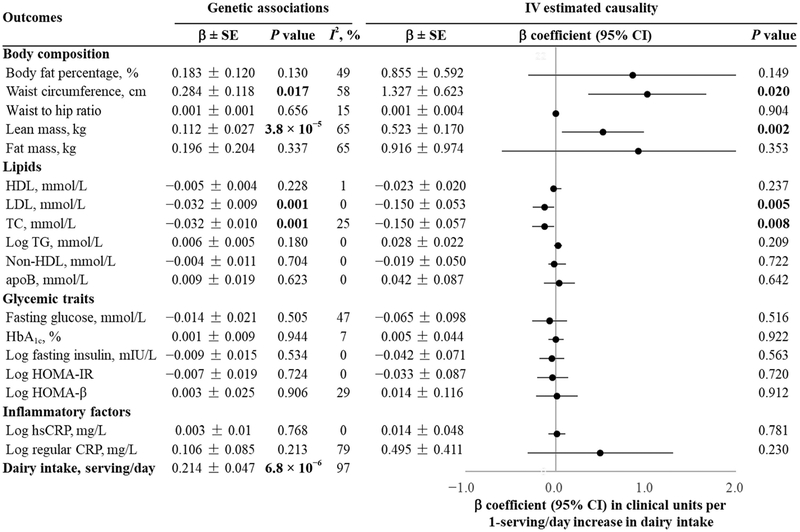
Fig. 3. Genetic association and estimated causality between dairy intake and cardiometabolic traits.
The LCT-13910 C/T located in upstream of the lactase (LCT) gene was selected as an instrumental variable. The MR estimate was computed from the ratio of the coefficient of the association between the LCT-13910 C/T and cardiometabolic traits to that of the association between the LCT-13910 C/T and dairy intake. This IV estimate reflects the potential causal effect of dairy intake on BMI. We pooled β coefficients across studies using random-effects (I2 ≥ 25%) or fixed-effects (I2 < 25%) meta-analyses based on the heterogeneity between studies.