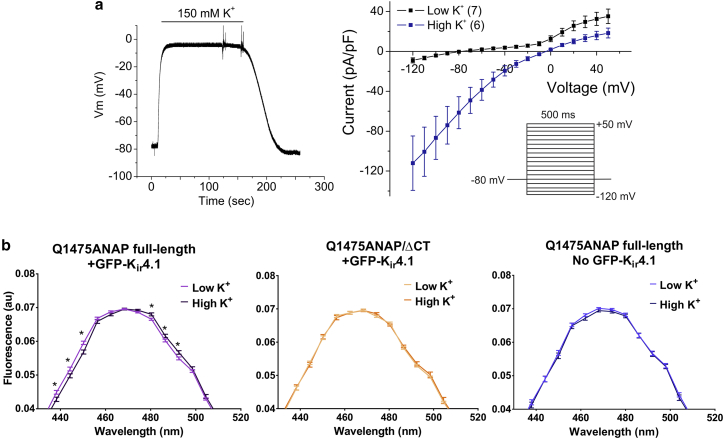
Figure 5.
A K+-depolarization ANAP spectral imaging assay of Nav1.5 conformational change. (a) Establishment of K+ depolarization to control RMP is shown. (Left) Representative current-clamp trace of GFP-Kir4.1 HEK293T stable cells is shown. Range in Vm is −80 to 0 mV with increasing [K+]ext from 5 to 150 mM. (Right) Reversal potential of GFP-Kir4.1 cells can be changed from −80 mV in low K+ (5 mM [K+]ext) to ∼0 mV in high K+ (150 mM [K+]ext). Error bars are ± SEM. Inset is the voltage protocol. (b) Spectra of full-length Nav1.5(Q1475ANAP) (left) and Nav1.5(Q1475ANAP/ΔCT) (middle) in cells expressing GFP-Kir4.1 and Nav1.5(Q1475ANAP) in cells with no GFP-Kir4.1 (AGFP/SAR < 0.3) (right), at low K+ and high K+, are shown. Q1475ANAP low K+, n = 36 cells; Q1475ANAP high K+, n = 30 cells; Q1475ANAP/ΔCT low K+, n = 21 cells; Q1475ANAP/ΔCT high K+, n = 19 cells; Q1475ANAP no GFP-Kir4.1 low K+, n = 18 cells; Q1475ANAP no GFP-Kir4.1 high K+, n = 16 cells. Error bars are ± SE of the average relative brightness of the channel. Spectra are zoomed in on the peak. ∗p-values (left to right) full-length Nav1.5(Q1475ANAP): p = 0.02, 0.02, 0.0009, 0.008, 0.04, 0.01, Student’s t-test. To see this figure in color, go online.