Figure 2.
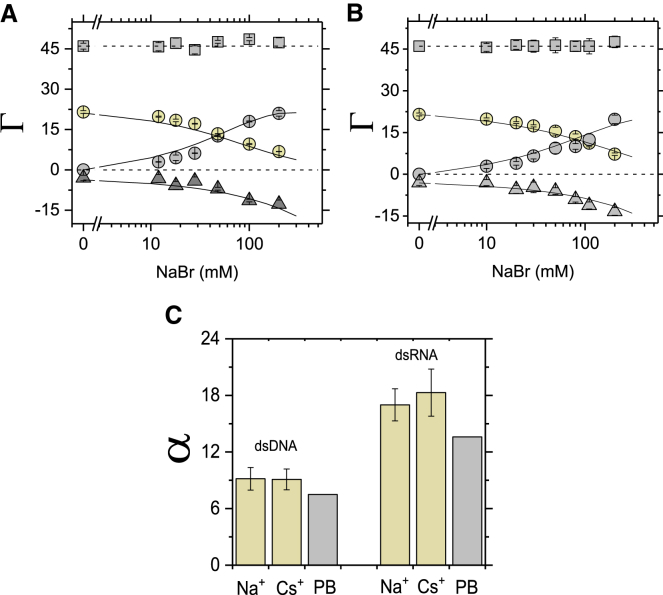
Competitive association of monovalent cations against Mg2+ for a 24-bp DNA and RNA duplexes. (A and B) The preferential interaction coefficient (Γ) of associated Na+ cations (gray circles), replaced Mg2+ cations (yellow circles, [MgBr2] = 6 mM), and excluded Br− anions (gray triangles) around the 24-bp DNA (A) and around the 24-bp RNA (B) are shown. In (A) and (B), the total charge of the ion atmosphere summed from the individual ion measurements is shown as squares, and the dashed lines at Γ = +46 represent the charge needed to neutralize the total 24-bp DNA and 24-bp RNA charge of −46e. Solid lines are PB calculations. (C) Shown are coefficients for monovalent cations against Mg2+ (Eq. 6), where CC is the concentration of competing cation at which the number of the competing cation and Mg2+ ions within the ion atmosphere are equal, [Mg2+] is the background concentration (here [Mg2+] = 6 mM). Each data point in (B) and (C) with the 24-bp RNA is the average of three independent measurements. Error bars are as in Fig. 1. See Table S4 for data and Tables S5 and S6 for PB calculations. Ion counting data for the 24-bp DNA (A) and (C) are from (30), where the same methodology was used. To see this figure in color, go online.