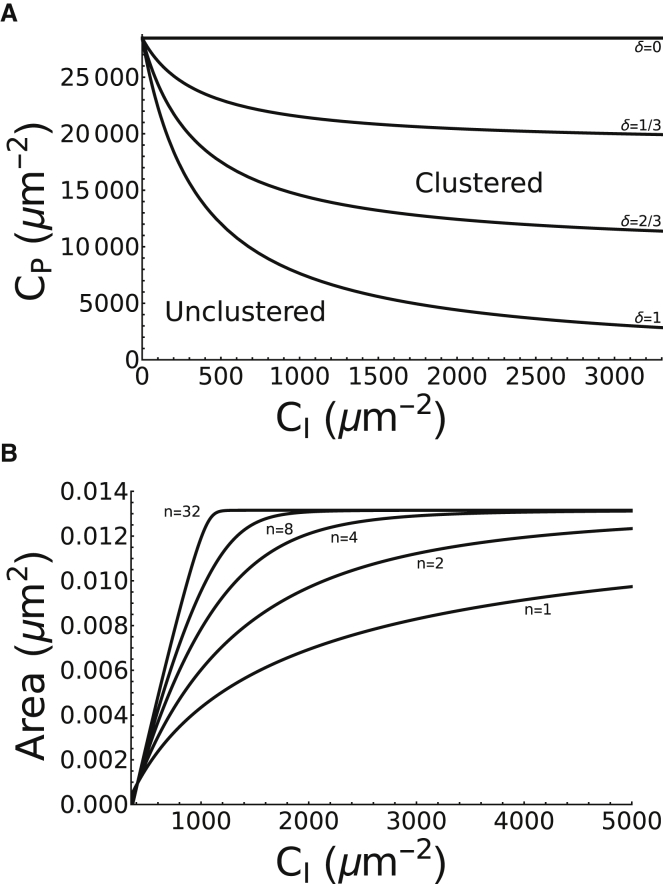
Figure 4.
The effects of coaggregation and cooperativity on steady-state dynamics of protein clustering. (A) Two-parameter bifurcation of adhesion area A with respect to CI and CP are given, showing the boundary between the regimes of unclustered (below) and clustered (above) steady states for various values of coaggregation δ. The boundary is defined by the transcritical bifurcation points in Fig. 3 when CI and CP are both varied. Increasing δ reduces the adaptor protein density needed to induce aggregation. In the limit δ → 0, integrin density CI has no effect on the aggregation of adaptor proteins. (B) Stable branches of the clustered steady states shown in Fig. 3A for various degrees of cooperativity n are given. By increasing n, the density thresholds for clustering decreases, and the steepness of the stable branch of clustered steady states increases.