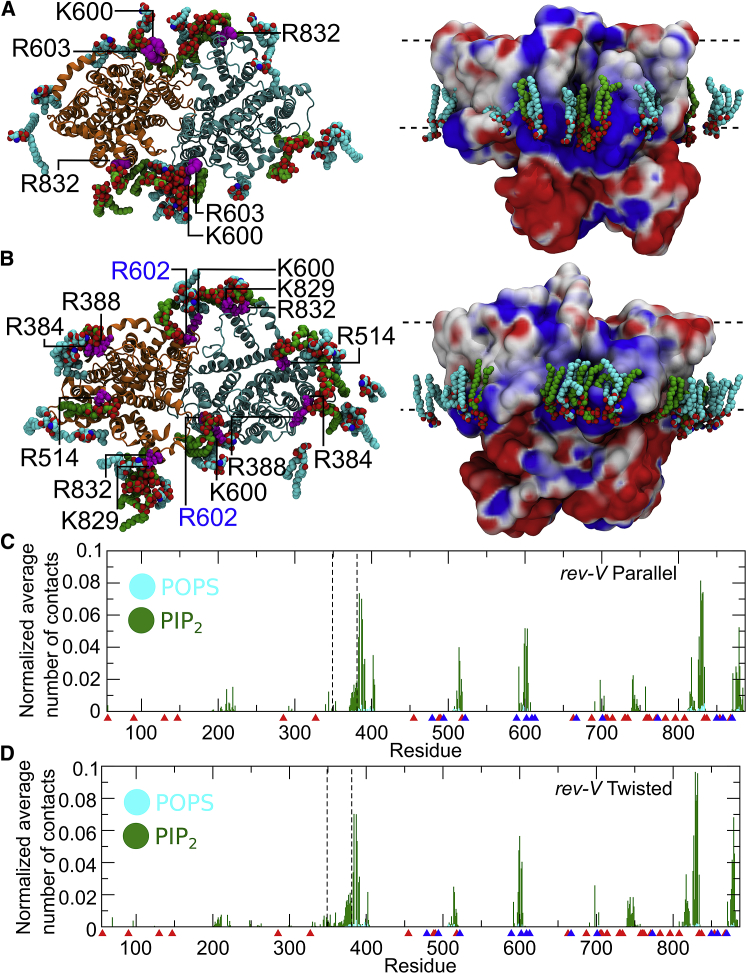
Figure 6.
Interaction of AE1 with anionic lipids. rev-V models in parallel and twisted conformation are shown in (A and B), respectively. The structures are the first centroid from the cluster analysis from the atomistic simulations in the native lipid mixture. The cdAE1 has been omitted for clarity in the view from the cytoplasmic side on the left. Positively charged residues from each chain involved in H-bonds in both subunits with PIP2 (green) and POPS (cyan) are shown in magenta (Table S3). On the right, surface representation of the AE1 dimer (side view), colored based on the electrostatic potential in aqueous solution at pH 7, calculated using APBS (57), with positive shown blue, neutral white, and negative red. The residue Arg602 causing AD-dRTA when mutated (76) is indicated in blue. The PIP2 and POPS lipids from this snapshot that interact with the protein are also shown. Plots in (C and D) show the normalized average number of contacts (within a cut-off distance of 0.55 nm) between AE1 and the headgroups of PIP2 (green) and POPS (cyan) lipids in the bilayer (across all CG-MD repeat simulations). For the normalization, the number of contacts of a residue with a lipid type was divided by the number of lipids and the number of frames. See also Fig. S11 and Table S3. To see this figure in color, go online.