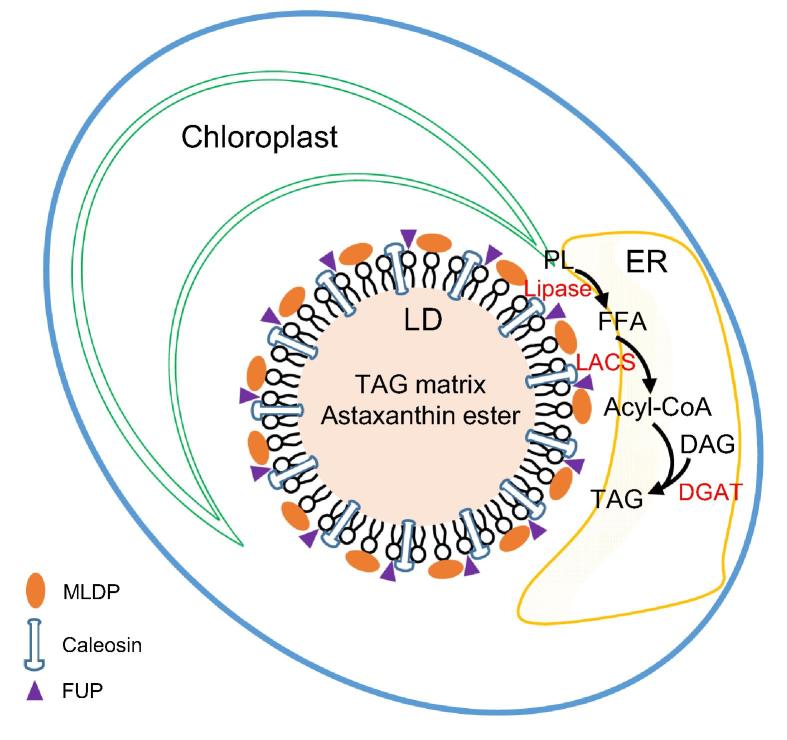
Figure 6.
A proposed model for C. zofingiensis LDs
LDs are in close contact with ER and chloroplast, enveloped and decorated with many structural proteins and functional enzymes. Structural proteins, e.g., MLDP, caleosins, and certain functionally unknown proteins, are shown to be associated with the PL monolayer of LDs, maintaining the stability of LDs. Enzymes involved in lipid metabolism such as PL lipase and LACS, working in concert with other lipid metabolism-related enzymes localized in ER (e.g., DGAT), contribute to lipid homeostasis. DAG; diacylglycerol; DGAT, diacylglycerol acyltransferase; MLDP, major lipid droplet protein; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; FFA, free fatty acid; FUP, functionally unknown protein; LACS, long chain acyl-CoA synthetase; LD, lipid droplet; PL, polar lipid; TAG, triacylglycerol.