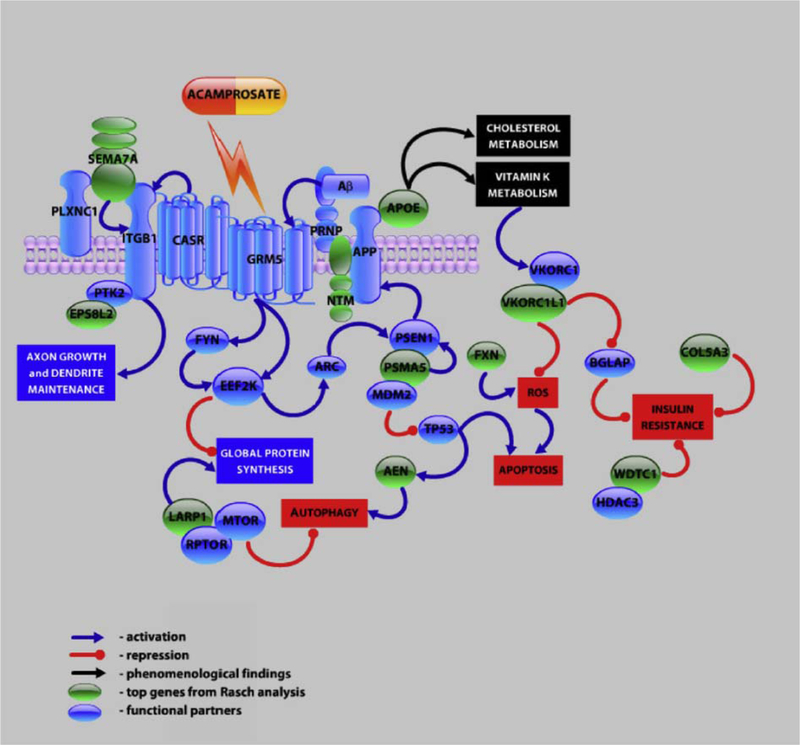
Fig. 14.
Hypothetical signaling network integrating top genes identified through Rasch analysis. A Rasch model was applied to the genes of ADNI GWAS data and supports APOE as a major susceptibility gene for AD, and functionally links other top genes (AEN, ADANTS12, PSMA5, FXN, NTRN, LARP1, WDTC1, SEMA7A, VKORC1L1, COL5A3) to AD. A hypothetical signaling network was generated from a pathway analysis of these genes based on known proteinprotein, functional, and phenomenological interactions. Abbreviations: AD, Alzheimer’s disease; ADNI, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative; ARC, activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein; EEF2K, eukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase, activated by GRM5 receptor, regulates global protein synthesis; HDAC3, histone deacetylase; MDM2, negative modulator of TP53 tumor suppression gene; PLXNC1, plexin C1 receptor for semaphorins; PTK2: FAK, kinase implicated in integrin signaling; FYN, src family tyrosine kinase, downstream target of GRM5 receptor; RPTOR, regulatory protein associated with MTORC1 complex. Reproduced with permission from [202].