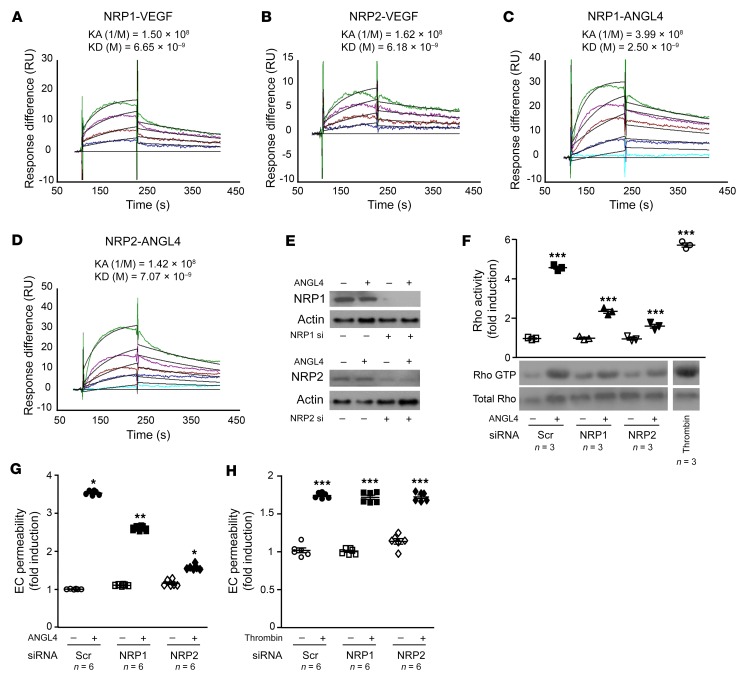
Figure 7. NRP1 and NRP2 bind ANGPTL4 and mediate its promotion of Rho activation and EC permeability.
(A–D) Representative sensorgrams of 3 experiments showing binding of VEGF and ANGPTL4 to immobilized NRP1 and NRP2, using SPR binding analysis. KA and KD constants are shown. Ligand concentrations used are 6.25 nM, 12.5 nM, 25 nM, and 50 nM for binding of VEGFA to NRP1 (A) and NRP2 (B); 3.125 nM, 6.25 nM, 12.5 nM, 25 nM, and 50 nM for binding of ANGPTL4 to NRP1 (C); and 3.125 nM, 6.25 nM, 12.5 nM, 25 nM, and 50 nM for binding of ANGPTL4 to NRP2 (D). RU, resonance units. The complete kinetics analysis is listed in Supplemental Table 3. (E) HUVECs were transfected with 50 nM scrambled siRNA, 50 nM NRP1 siRNA, or 50 nM NRP2 siRNA. Inhibition of NRP1 and NRP2 expression is shown. Levels of NRP1, NRP2, and actin were determined in gels run in parallel. (F) Rho activation assay upon transfection of scrambled siRNA, NRP1 siRNA, or NRP2 siRNA and treatment with 5 μg/mL rhANGPTL4 in HUVECs. Positive control: 0.5 U/mL thrombin. (G and H) EC permeability assay upon transfection of scrambled siRNA, NRP1 siRNA, or NRP2 siRNA and treatment with 5 μg/mL rhANGPTL4 (G) or 0.5 U/mL thrombin (H) in HUVECs. One-way ANOVA (F, G, H). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Experiments were repeated at least 3 times.