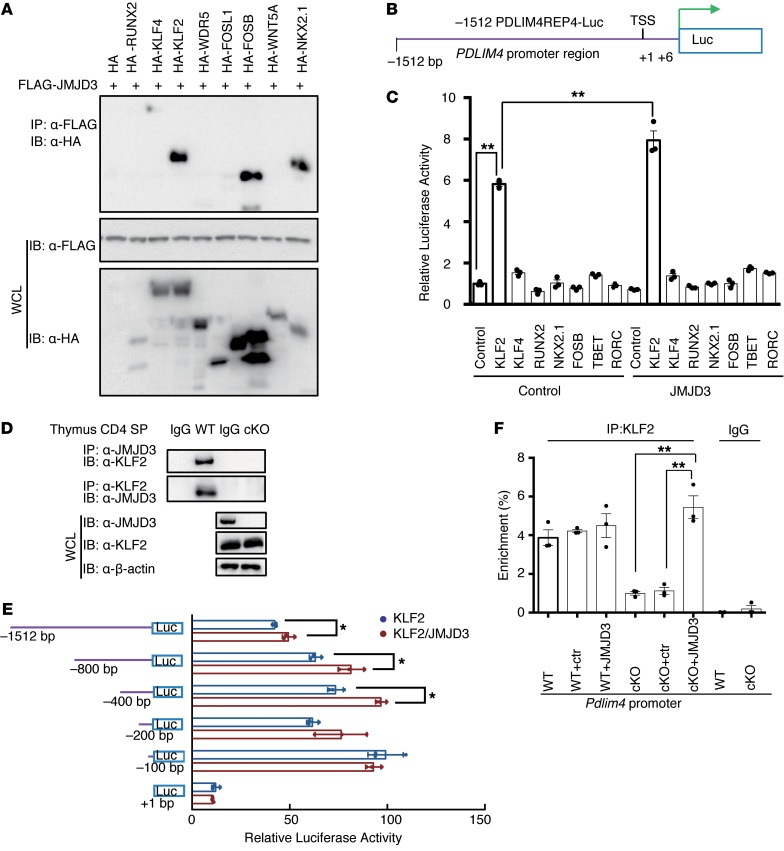
Figure 5. JMJD3 regulates Pdlim4 expression by interacting with KLF2.
(A) Screening of transcription factors interacting with JMJD3. 293T cells were cotransfected with HA-tagged Runx2, Klf4, Klf2, Wdr5, Fosl1, FosB, Wnt5a, Nkx2.1, and FLAG-Jmjd3. WCLs were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG Abs and immunoblotted with anti-HA Abs. (B) Schematic presentation of the Pdlim4 promoter–driven luciferase construct. The promoter region –1512 bp upstream was cloned into an episomal luciferase vector. (C) The transcriptional activity of proteins interacting with JMJD3 in regulating Pdlim4 was evaluated by dual-luciferase assay. Data are presented as mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments (n = 3). **P < 0.01, 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (D) Thymic CD4 SP T cells were isolated from WT and Jmjd3-cKO mice and immunoprecipitated with anti-JMJD3 or anti-KLF2 Abs and protein (A+G) beads. The immunoprecipitated product was immunoblotted with anti-KLF2 or anti-JMJD3 Abs. (E) Mapping the KLF2 and JMJD3 binding regions of the Pdlim4 promoter using a dual-luciferase assay. Different regions of the Pdlim4 promoter were cloned into the episomal luciferase vector and then were cotransfected with Klf2 and Jmjd3 into 293T cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments (n = 3). *P < 0.05, Student’s t test. (F) ChIP-qPCR analysis of percentage of enrichment of KLF2 at the Pdlim4 promoter in WT and Jmjd3-cKO thymic CD4 SP T cells after ectopic expression. Jmjd3 IgG was used as isotype control. n = 3. **P < 0.01, 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test.