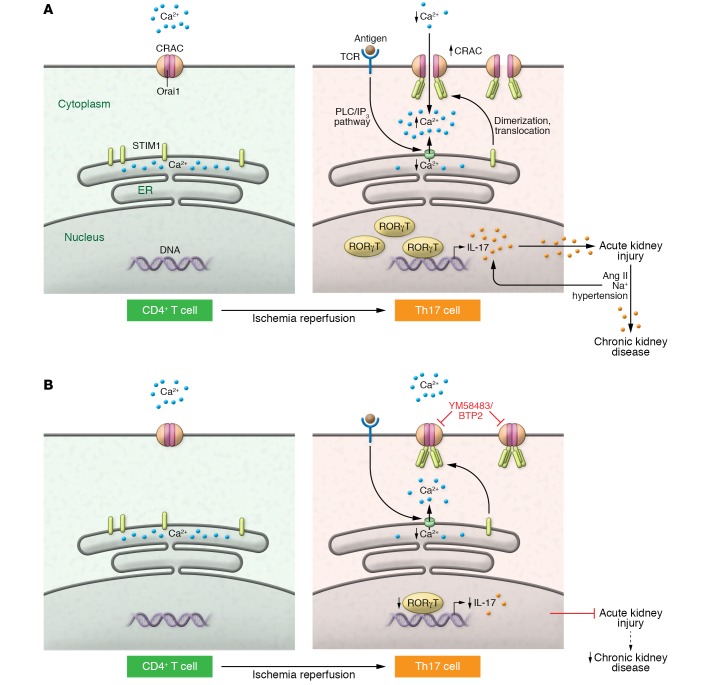
Figure 1. Major events during Orai1-mediated Th17 differentiation in AKI.
(A) In resting CD4+ T cells, Orai1 is in a closed confirmation and Ca2+ is confined to the ER lumen. Following IR, Orai1 expression increases. With subsequent increase in intracellular Ca2+, RORγT activity and IL-17 production drives Th17 differentiation and AKI pathogenesis. Simultaneously, antigen binding to the TCR triggers ER Ca2+ release, likely via the PLC/IP3 pathway. STIM1, sensing loss of ER Ca2+, translocates to the plasma membrane and activates CRAC protein, resulting in Orai1 opening. Exposure to high Ang II and Na+ following AKI reactivates the Th17 response in predominantly Orai1+ cells and sustains inflammation to drive AKI to CKD. (B) CRAC inhibitors, such as YM58483/BTP2, block Ca2+ influx through Orai1 and may protect from AKI and limit the AKI-to-CKD transition.