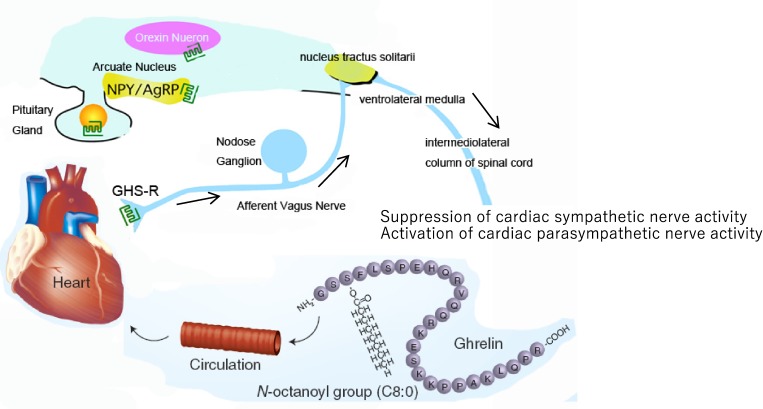
Figure 6.
(Color online) Schematic representation of the potential mechanism of ghrelin-mediated regulation of the cardiac autonomic nervous system. By acting on the cardiac vagal afferent nerve terminals, which send signals to the vasomotor center of the medulla through the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS; shown by arrows), peripheral ghrelin inhibits cardiac sympathetic nerve activity and activates cardiac parasympathetic nerve activity in cardiac disease, which may protect the heart from excessive damage. Adapted from Tokudome et al.38) AgRP: agouti-related peptide, NPY: neuropeptide Y, GHS-R: growth hormone secretagogue receptor.