Figure 1. Directed IFITM expression inhibits HCV infection in cell culture.
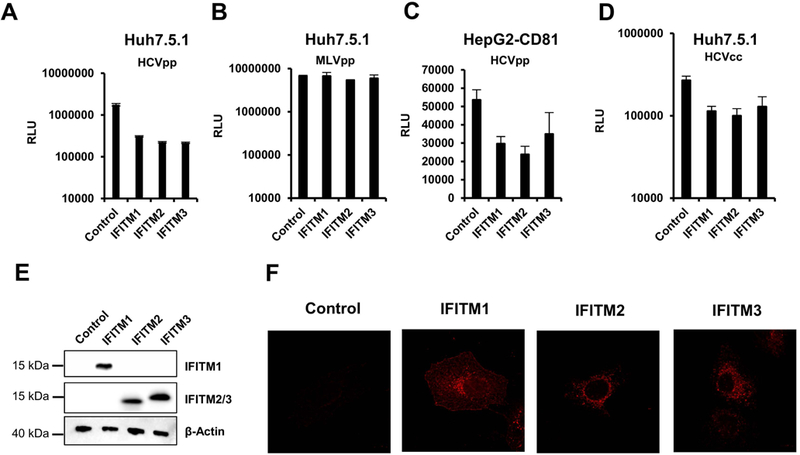
Huh7.5.1 (A and B) or HepG2-CD81 (C) cells were transduced with vectors encoding the indicated IFITM proteins or were transduced with empty vector as control. Transduced cells were then infected with HCVpp of GT1b (A), GT1a (C) or with MLVpp (B). Infection was assessed after 72 h by measuring luciferase activity. Individual representative experiments are shown. Error bars represent SD. Similar results were obtained in more than three independent experiments. (D) Huh7.5.1 cells stably expressing IFITMs were infected with HCVcc Luc-Jc1. Infection efficiency was assessed after 72 h by measuring luciferase activity. Shown is a representative of three independent experiments, error bars indicate SD. (E) Expression of IFITM proteins in Huh7.5.1 cells was assessed by immunoblot using IFITM-specific antibodies. β-Actin is used as loading control. One representative western blot is shown (F). Huh7.5.1 cells transduced with IFITM1–3 or a control vector were stained with a mouse anti-IFITM1 or a rabbit anti-IFITM2 antibody (IFITM2 and 3).
