Figure 2. Differential sensitivity of acute and chronic HCV variants to inhibition by IFITM proteins.
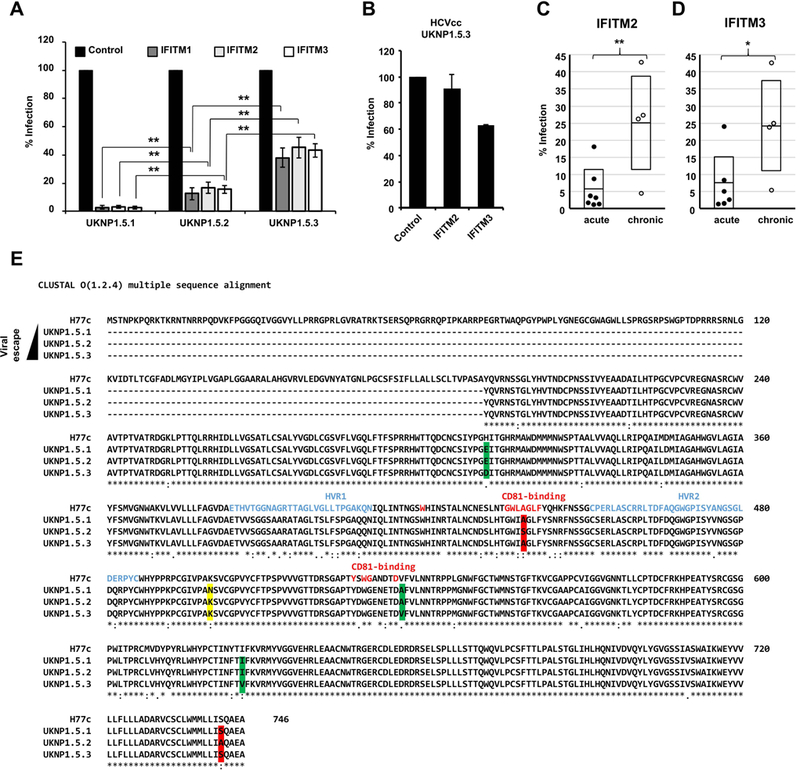
Huh7.5.1 cells were transduced to express the indicated IFITM proteins and then infected with HCVpp bearing envelope proteins derived from acute or chronic patients. (A) Analysis of the IFITM-sensitivity of sequential envelope variants (UKNP1.5.1 pre-seroconversion; UKNP1.5.2 acute phase, two months later; UKNP1.5.3 chronic phase, 7 months later), isolated from a single HCV patient. (B) TCID50 analysis of UNKP1.5.3 HCVcc infection of transduced IFITM-expressing Huh7.5.1 cells. Shown are means of two experiments performed in sextuplicates. Error bars represent SD. (C) and (D) E1E2 patient variants isolated from patients with acute or chronic HCV infection of genotype 1A and 3. Each dot represents the result for a single envelope variant and IFITM2- (C) or IFITM3-expressing (D) Huh7.5.1 cells. Shown are the means of three experiments conducted in triplicates. Error bars represent SEM. Control was set to 100%. *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 using one-sided students T-test. (E) Clustal O Alignment of the protein sequences of H77c, UKNP1.5.1, UKNP1.5.2 and UKNP1.5.3. The sequences were obtained from GenBank. Changes highlighted in yellow are unique for UKNP1.5.1, changes in green are only present in UKNP1.5.2 and changes highlighted in red are unique for UKNP1.5.3. HVR1 and 2 are indicated in blue, red letters mark key positions for CD81-binding.
