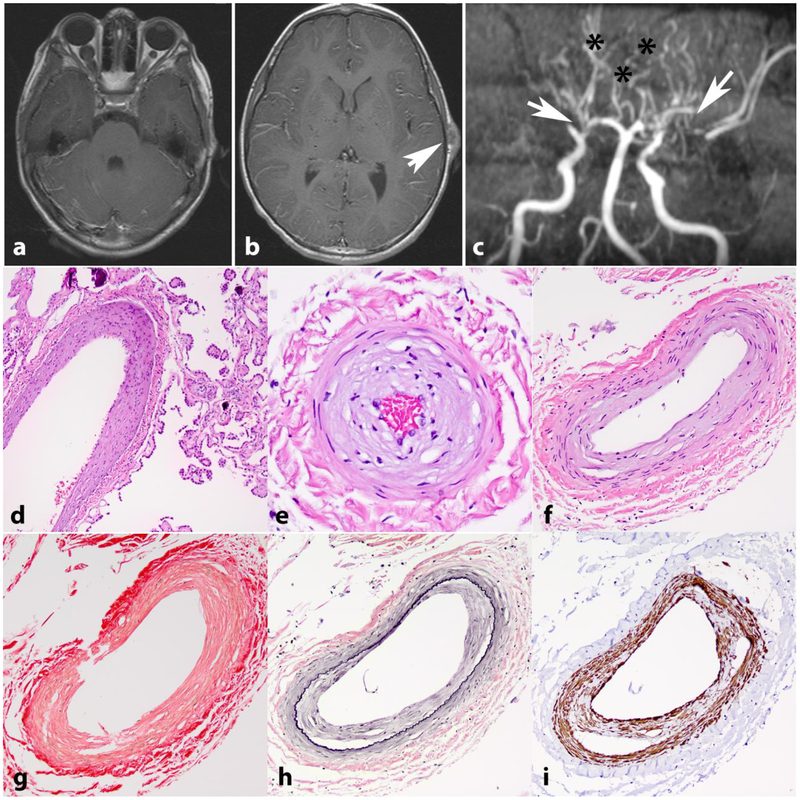
Figure 2. Intracranial vasculopathy in NF1.
Axial T1 weighted image with contrast in a 15-year-old boy with NF1 shows bilateral optic nerve gliomas, larger on the right (a). Axial T1 weighted image with contrast also shows a left frontoparietal scalp soft tissue lesion representing a cutaneous neurofibroma (arrow) (b). MR angiography of the circle of Willis shows stenosis of the distal internal carotid arteries, with no flow in the right middle cerebral artery and severe narrowing of the left middle cerebral artery (arrows). Many collateralized vessels in a moya-moya pattern are seen (asterisks) (c). Histologic sections from a 21 year-old patient with NF1 demonstrating intimal thickening involving vessels in the choroid plexus (d) and leptomeninges (e,f). Picrosirius red stain demonstrates normal mural collagen fiber architecture (g). VVG highlights intimal hyperplasia central to internal elastic lamina (black)(h) and SMA immunostain shows positivity in many of these cells (i).