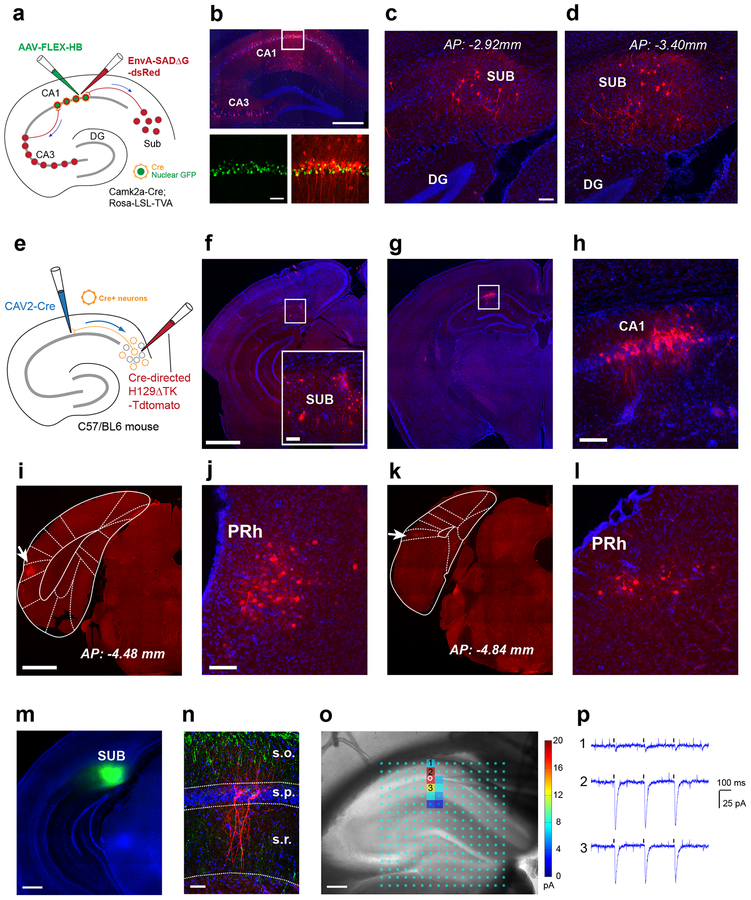
Fig. 1. The cortico-hippocampal circuitry involving a non-canonical subiculum - CA1 pathway is identified anatomically by retrograde monosynaptic rabies tracing and anterograde herpes simplex virus (H129) tracing, and verified functionally by channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) assisted circuit mapping.
a-d, Direct subiculum-CA1 backprojections are shown by monosynaptic retrograde rabies tracing. This experiment was independently repeated in 12 mice, each with similar results. a, The scheme for our Cre-dependent, monosynaptic rabies tracing approach (see details in the Methods). Using Camk2a-Cre; TVA mice, we map direct presynaptic input connections onto Camk2a-Cre expressing excitatory neurons in hippocampal CA1 in the intact brain. Starter neurons in dorsal hippocampal CA1 are shown (b, top panel), labeled by both EGFP and dsRed expression from both AAV and rabies infection (b, bottom panels). Their presynaptic partners (e.g., local interneurons and CA3 neurons) are labeled by the red fluorescent protein dsRed from rabies infection. The scale bars for the top and bottom panels are 500 μm and 50 μm. c-d, Retrogradely labeled subicular neurons presynaptic to CA1 excitatory neurons are seen in sections of dorsal subiculum at different anterior-posterior positions (c, AP: −2.92 mm; d, AP: −3.40 mm). Scale bar = 50 μm. e-h, Time-limited anterograde-directed HSV tracing supports subiculum-CA1 projections. This experiment was independently repeated in 5 mice, each with similar results. e, The scheme for anterograde tracing by combined use of CAV2-Cre injection in CA1 and the injection of Cre-dependent H129 (H129ΔTK-tdTomato) in SUB to map projections of CA1-projecting SUB excitatory neurons. f, H129 infected neurons at the injection site in the subiculum are shown in red; DAPI staining in blue. The scale bar on the left (1mm) applies to the lower magnification panels while the scale bar for the enlarged insert panel on the right is 200 μm. g-h, Postsynaptic neuronal labeling is robustly seen in hippocampal CA1 ipsilaterally at 48 hours post H129 viral injection. Scale bar = 200 μm in h. i-l, Besides CA1, postsynaptic neuronal labeling by H129 is seen in the perirhinal cortex (PRh) ipsilaterally. This experiment was independently repeated in 5 mice, each with similar results. i, An example of perirhinal labeling, with a white arrow pointing to the atlas aligned brain structure of PRh. The scale bar (1mm) applies to both i and k. j, An enlarged view of perirhinal neuronal labeling in i. The scale bar (200 μm) applies to both j and l. k-l, Perirhinal labeling from a different animal. m-p, Physiological mapping indicate that CA1 pyramidal neurons receive excitatory subicular inputs. This experiment was independently repeated in 8 cells from 5 mice, each with similar results. m, Spatially localized iontophoretic injection of AAV1-ChR2-Venus in the subiculum (green). n, Post-hoc verification of biocytin-filled recorded pyramidal neurons (red) along with the distribution of ChR2/Venus expressing subicular axons (green) counterstained with DAPI in a hippocampal slice. o-p, Direct subicular innervation of CA1 excitatory neurons is shown by postsynaptic current responses to local photoactivation of ChR2-expressing subicular axons in the presence of TTX and 4-AP, which block Na+ channels required for generating axonal action potentials and K+ channels critical for axonal membrane potential repolarization, respectively. o, Highly localized excitatory subicular inputs impinged onto the recorded excitatory pyramidal neuron (indicated by the white circle). The photoactivation sites (light cyan dots) are superimposed on the slice image, with the strength of evoked input sites scored with a color coded heat map for average integrated input strength within the analysis window (>10 ms to 160 ms post photostimulation), with the baseline spontaneous responses subtracted from the photostimulation response of the same site (for more details see Methods). p, Raw ChR2 photoactivation responses recorded from the pyramidal neuron in response to 3 repeated laser flashes (473 nm, 1 ms) at the oriens (1), pyramidale (2), and radiatum (3) layer of CA1, respectively.