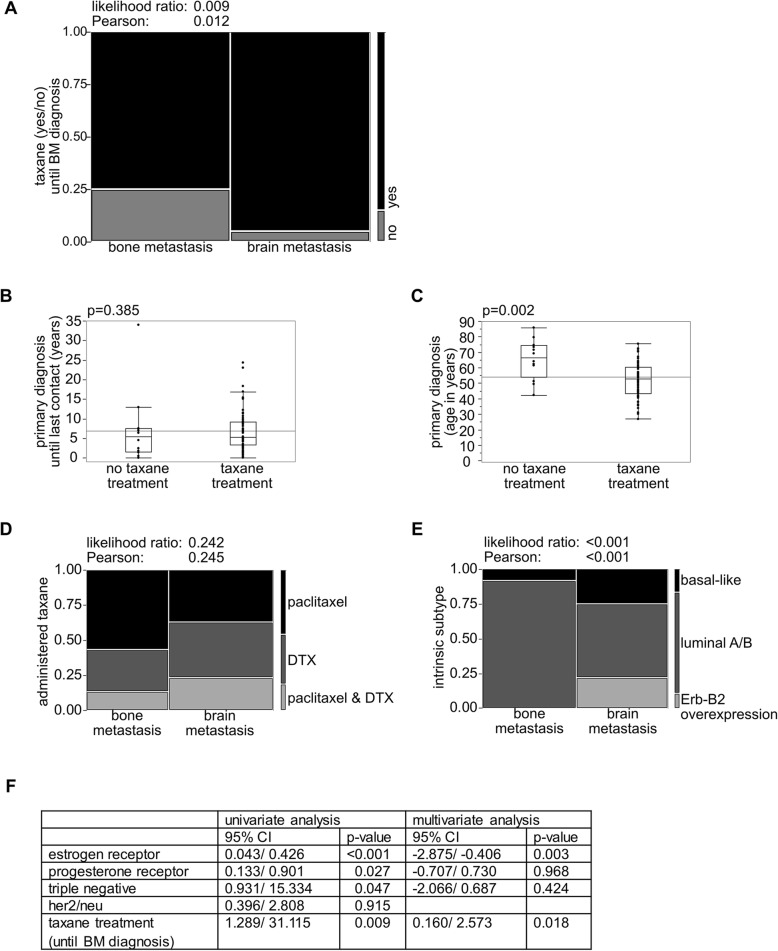
Fig. 1.
Incidence of CNS-involvement is increased in taxane-treated mBC patients. a Contingency analysis with likelihood-ratio and Pearson test of taxane-treatment (yes/no) for BM- vs. nBM-cohort. b, c Non-parametric multiple comparisons for each pair using Wilcoxon-method: b Follow up “primary diagnosis” (N (notaxane) = 12, N (taxane) = 68); c Patient age primary diagnosis (N (notaxane) = 12, N (taxane) = 68). d, e Contingency analysis with likelihood-ratio and Pearson test of (d) administered taxane (N (nBM) = 30, N (BM) = 38, N varies from 40 as the non-taxane-treated subcohort was excluded for the analysis) and (e) intrinsic subtypes (N (nBM) = 40, N (BM) = 40) for BM- vs. nBM-cohort. f For univariate analysis, effect likelihood ratio and odds ratio test was used; for multivariate analysis nominal logistic fit for the endpoint BM-development using effect likelihood ratio test was applied. Statistical analysis was performed using JMP 14.0.0 software (SAS)