Fig. 1.
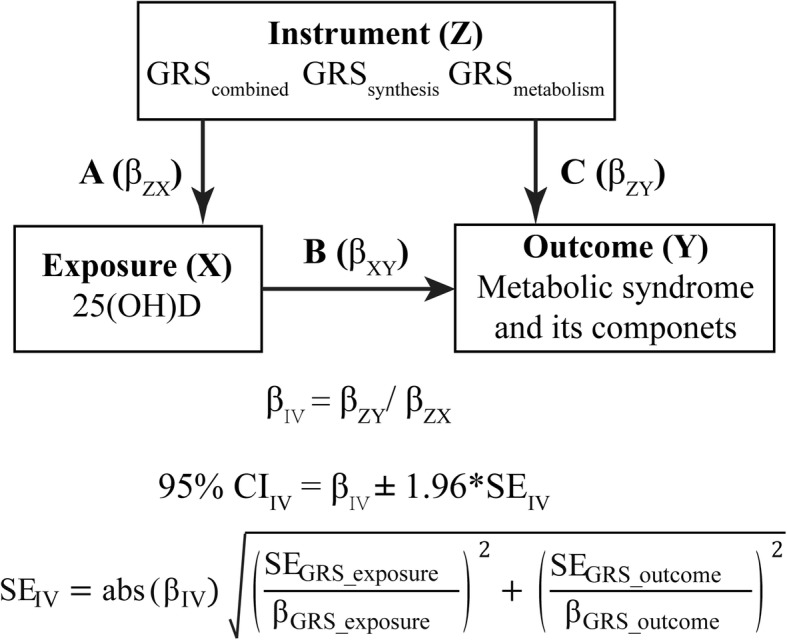
Study design and tested associations. GRS, genetic risk score; 25(OH)D, 25-hydroxyvitamin D; IV, instrumental variable. We assessed the association between vitamin D related genetic variants and 25(OH)D concentrations (a). Second, we measured the effects of genetic variants associated with 25(OH)D on the changes of metabolic components and MS risk (c). Third, we did observational assessments of the relation between 25(OH)D concentrations and present MS and its components (b)
