FIGURE 2.
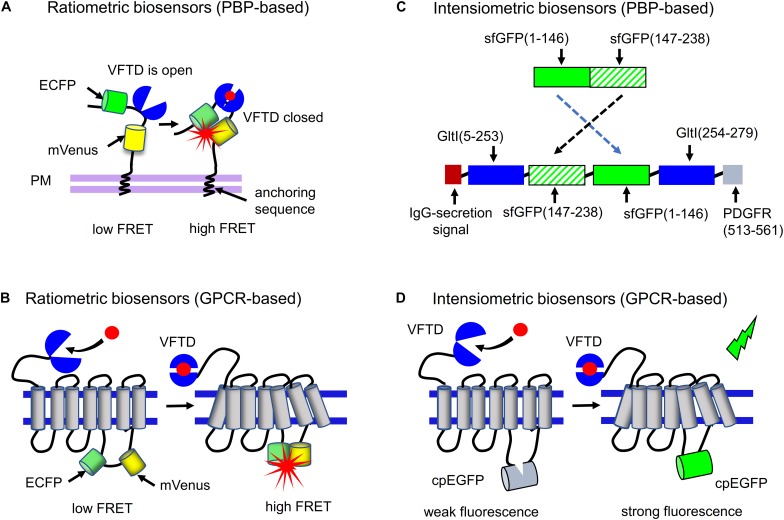
Ratiometric and intensiometric biosensors. (A) FRET-based biosensors in which PBP proteins are used as neurotransmitter-sensing domains. A PBP is inserted between FRET pair of FPs, such as ECFP and mVenus. Upon PBP interaction with neurotransmitter the FRET efficiency between FPs changes, which can be detected. (B) FRET-based biosensors in which GPCR receptors are used as neurotransmitter-sensing domains. A FRET pair consisting of ECFP and mVenus is inserted in the third intracellular loop of the respective GPCR. Upon interaction of the receptor with neurotransmitter FRET between two FPs changes. (C) Example of the PBP-based intensiometric biosensor is shown. Circular permutant of superfolder GFP (sfGFP) between positions 146–147 is inserted into GltI protein, resulting in the SF-iGluSnFR glutamate biosensor (Marvin et al., 2018). N-terminal IgG-secretion signal ensures transport of the biosensor to extracellular space, while C-terminal transmembrane domain of PDGFR receptor anchors the biosensor to the plasma membrane (D) Example of the GPCR-A-based intensiometric biosensor is shown. Circularly permuted EGFP (cpEGFP) is inserted into the third intracellular loop of GPCR having the VFTD domain at the N-terminus. After binding neurotransmitter or neuromodulator, the conformation of GPCR changes that results in enhancement of cpEGFP fluorescence.