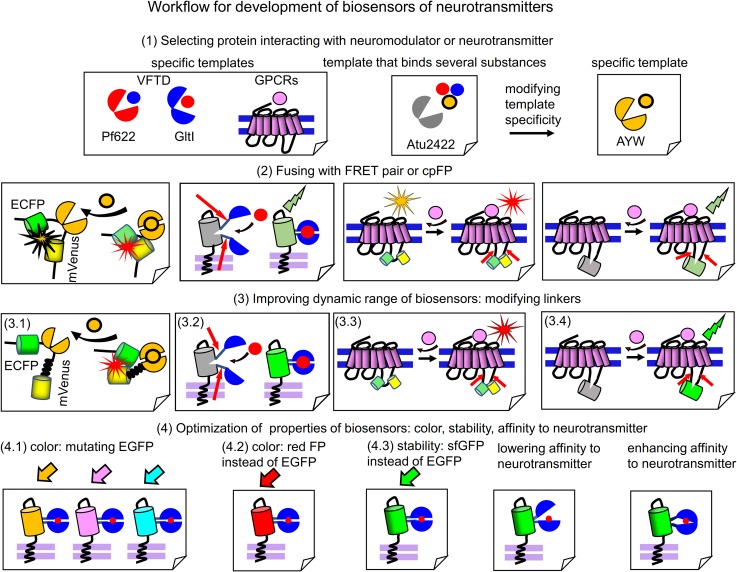
FIGURE 3.
Workflow for engineering of biosensors. (1) Selection of a protein template, which interacts with the respective neurotransmitter or neuromodulator. From left to right: specific templates that bind relevant chemical substance with high specificity, such as GPCRs, GltI from Escherichia coli or Pf622 from Pseudomonas fluorescens. A promising template, such as Atu2422 from Agrobacterium tumefaciens that binds glycine, GABA and L-serine is also shown. Atu2422 mutant AYW binds only glycine and is used in glycine biosensor (Zhang et al., 2018). (2) Fusing of neurotransmitter-binding protein templates with FRET pairs of FPs or cpFPs. From left to right: Glycine-binding AYW is inserted between ECFP and mVenus; cpEGFP is inserted in the flexible region of GltI (Hires et al., 2008). FRET pair or cpFP is inserted in the third intracellular loop of GPCRs. Note the low dynamic range of relevant fusions. (3) Improving dynamic range of the initial fusions. (3.1) Deleting the flexible regions between ECFP and AYW in GlySF biosensor and inserting the rigid helical linker between AYW and mVenus (3.2) Mutagenesis of linkers joining VFTD domain and cpEGFP in a biosensor. (3.3 and 3.4) Mutagenesis of regions of the third intracellular loop of GPCRs in the point of insertion of FRET pair or cpFP. (4) Optimization of properties of resulting biosensors with high dynamic range. Manipulating color, stability and response dynamics. (4.1) Mutations, which change color of EGFP to yellow (mVenus), cyan (mTurquoise) and blue (mAzurite) are introduced in the cpEGFP-based biosensor to get a set of multicolor biosensors (Marvin et al., 2018). (4.2) EGFP is changed to mApple to get novel red fluorescent biosensor (Wu et al., 2018). (4.3) EGFP is changed to sfGFP to enhance biosensor stability. (4.3) Lowering affinity of the neurotransmitter-binding protein to the neurotransmitter allows to get biosensors able to detect fast neurotransmitter transients (Helassa et al., 2018; Marvin et al., 2018). (4.3) Enhancing affinity of neurotransmitter-binding protein allows to increase biosensor sensitivity to neurotransmitter (Marvin et al., 2018).