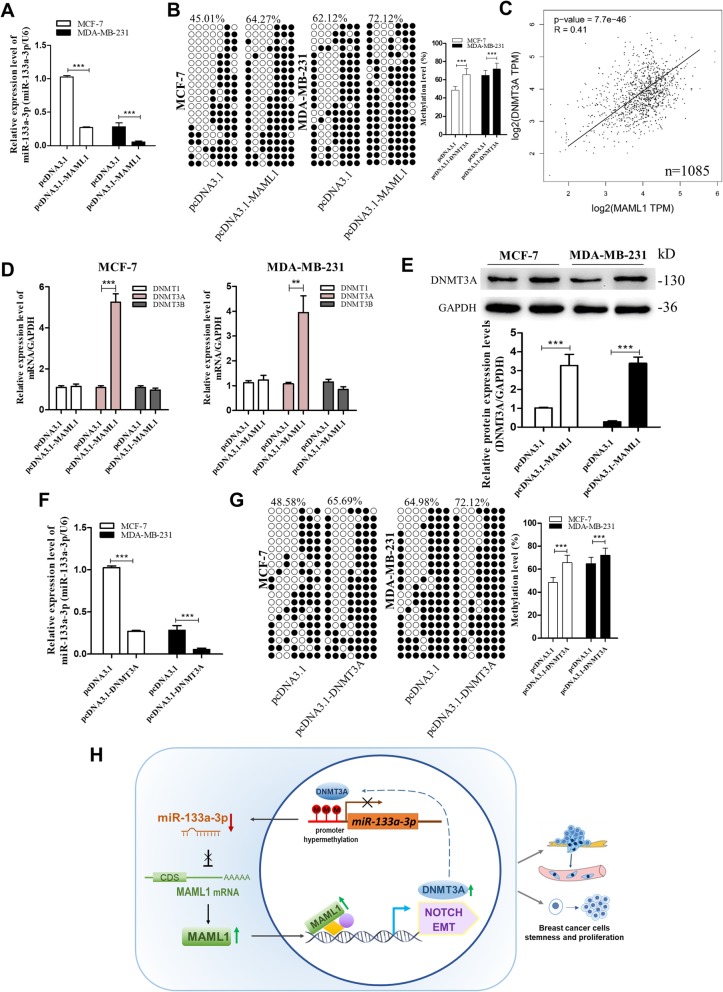
Fig. 8.
MAML1 feedback regulate methylation of miR-133a-3p through DNMT3A. a, b mRNA levels (a) and the methylation levels (b) of miR-133a-3p in MCF-7 cells and MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with either the pcDNA3.1 and pcDNA3.1-MAML1. c Pearson’s correlation analysis of the fold change of MAML1 mRNA and DNMT3A mRNA in 1085 human breast cancer tissues by GEPIA database from the TCGA project. d The mRNA levels of DNMT1, DNMT3A, and DNMT3B in MCF-7 cells and MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with either the pcDNA3.1 or pcDNA3.1-MAML1. e DNMT3A protein levels in MCF-7 cells and MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with either the pcDNA3.1 or pcDNA3.1-MAML1. f, g mRNA levels (f) and the methylation levels (g) of miR-133a-3p in MCF-7 cells and MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with either the pcDNA3.1 or pcDNA3.1-DNMT3A. h A working model for the role of MAML1-targeted miR-133a-3p in breast cancer metastasis. During breast tumorigenesis, silencing of miR-133a-3p mediated by DNA methylation facilitated proliferation, stemness, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells through up-regulating the expression of MAML1, which positively provided feedback for the methylation of miR-133a-3p. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001