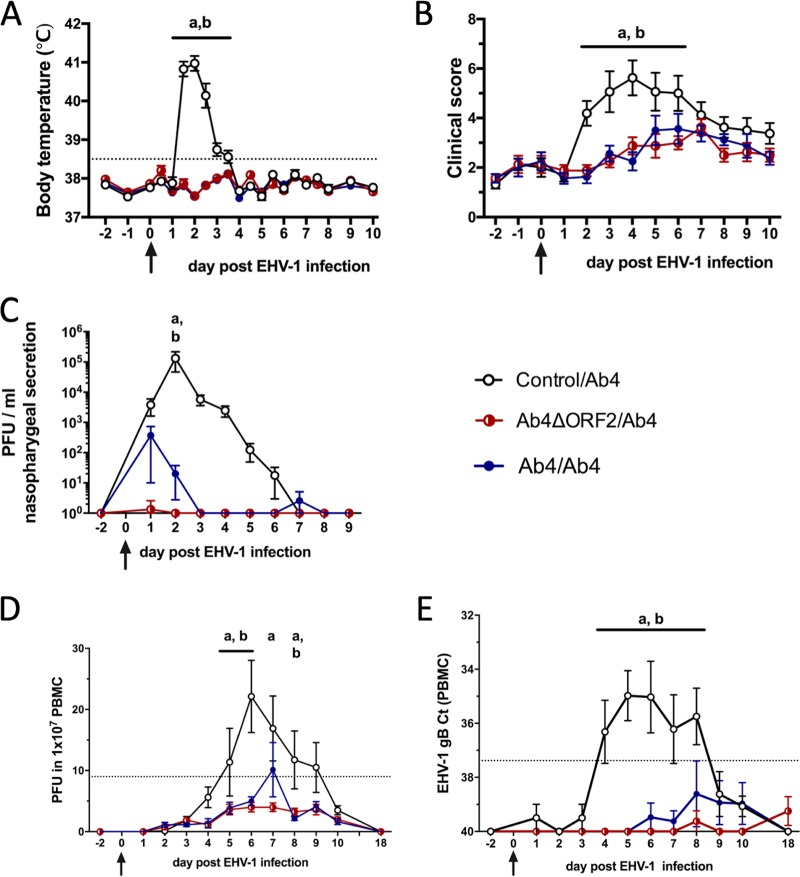
FIG 1.
Clinical disease and virus detection after EHV-1 challenge infection. A total of 24 horses were challenged intranasally with 1 × 107 PFU neuropathogenic EHV-1 Ab4 on day 0 (arrows). Nine months prior to challenge, these horses were initially infected intranasally with Ab4ΔORF2 (n = 8) or Ab4 (n = 8) or kept as controls without infection (n = 8). (A) Body temperature; (B) clinical score (range, 0 to 22) calculated as the sum of numerical scores for nasal discharge, ocular discharge, lymph node enlargement, ataxia, depression, and reduced appetite; (C) virus shedding (PFU/ml) in nasal secretions detected by virus isolation; (D) viremia detected by virus isolation in PBMC; (E) viremia detected by real-time PCR and shown as cycle threshold (CT) values. Mean and standard errors are plotted for each group. Dotted horizontal lines represent a cutoff of fever at 38.5°C (A), EHV-1 detection at 9 PFU (D), or 37.38 CT (E). Significant differences between groups are marked as a (control/Ab4 versus Ab4ΔORF2/Ab4) and b (control/Ab4 versus Ab4/Ab4).