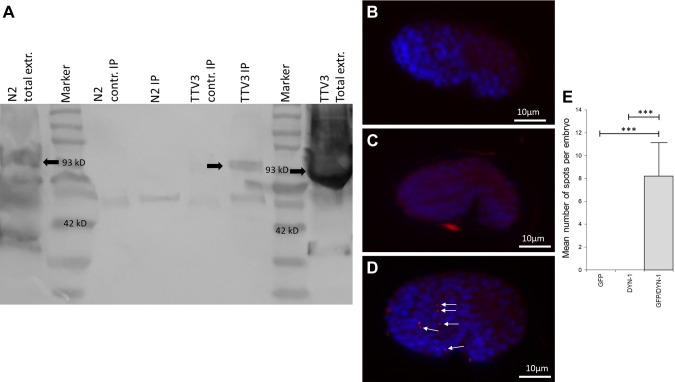
Figure 1.
A) The NM23 homolog NDK-1 functions in a complex with DYN-1 in C. elegan. IP of NDK-1 with DYN-1 was performed by anti-GFP Ab (3E6) or by anti-tubulin mouse IgG as a control (contr.). Detection was done using anti-Dynamin. Arrows indicate DYN-1 (C. elegans homolog, 93 kD). Lanes: N2 (wild-type) total extract (extr.); MW marker; N2 (wild-type) extract precipitated by nonspecific (anti-tubulin) mouse IgG; N2 (wild-type) extract precipitated by mouse monoclonal anti-GFP antibody (3E6); TTV3 (NDK-1::GFP–transgenic line) extract precipitated by nonspecific (anti-tubulin) mouse IgG; TTV3 (NDK-1::GFP–transgenic line) extract precipitated by mouse monoclonal anti-GFP antibody (3E6); MW marker; TTV3 (NDK-1::GFP–transgenic line) total extract. B–E) DPLA shows that NDK-1 and DYN-1 are colocalized in C. elegans comma-stage embryos. Freeze-cracked and fixed embryos transgenic for NDK-1::GFP were stained by anti–DYN-1 and anti-GFP antibodies, and then the Duolink assay was performed. During microscopy, comma-stage embryos were selected (lateral view, anterior left). Blue staining (DAPI) indicates nuclei, and red dots (highlighted by arrows) represent Duolink signal. The Duolink assay only gives a positive signal if both species-specific antibodies are added to the sample. Labeling only with anti-GFP antibody (negative control I) (B). Labeling only with anti–DYN-1 antibody (negative control II) (C). Labeling with anti–DYN-1 and anti-GFP antibodies (D). Error bar represents sem. ***Significantly different from controls, determined by Student’s t test (n = 10) (E).