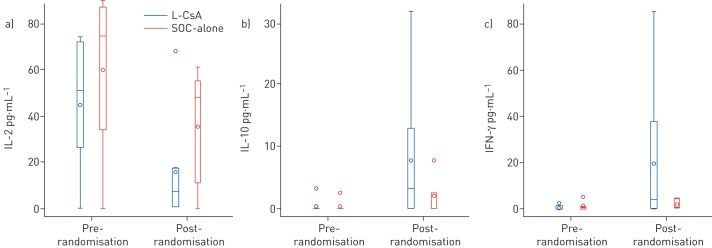
FIGURE 4.
A comparison of a) interleukin (IL)-2, b) IL-10 and c) interferon (IFN)-γ cytokines between the liposomal cyclosporine (L-CsA) and standard of care (SOC)-alone arms, pre- and post-randomisation during the 48-week follow-up. Data are presented as median with interquartile range (IQR) (boxes), together with minimum and maximum values (whiskers); the circle within a box represents the mean, while circles outside of a box represent outliers. Compared with SOC-alone, the post-randomisation changes in IL-2, IL-10 and IFN-γ (analysed by two-way ANOVA) were significantly different in the L-CsA group, with post-randomisation values (median (interquartile range)): IL-2 7.1 (0.5–17.1) pg·mL−1 in L-CsA versus 48.4 (11.3–55.2) pg·mL−1 in SOC-alone (p=0.04), IL-10 3.3 (0–13.0) pg·mL−1 in L-CsA versus 0 (0–2.5) pg·mL−1 in SOC-alone (p=0.04) and IFN-γ 3.8 (0.2–37.6) pg·mL−1 in L-CsA versus 0.8 (0.7–4.4) pg·mL−1 in SOC-alone (p=0.05). All other cytokines measured, including IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-17 and tumour necrosis factor-α, showed no significant differences post-randomisation between patients randomised to L-CsA versus SOC-alone.