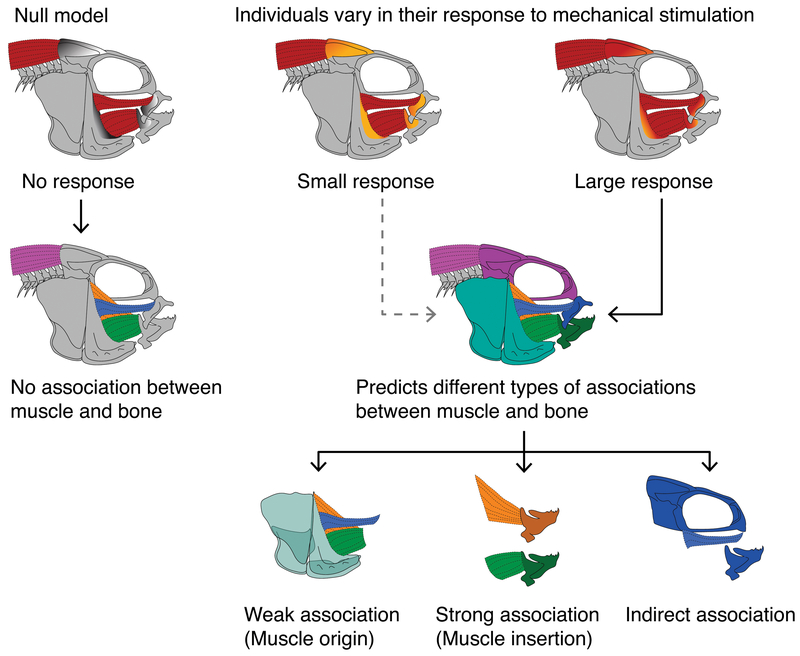
Figure 1.
Predictions for the types of associations that we may observe between muscles and bones, and how they arise. Our null model suggests that bone does not have the capacity to respond to mechanical stimulus, based on muscle volume, such that no associations will exist between bone shape and muscle volume. Our alternative model suggests that, based on the degree of mechanical stimulus or the extent to which bone can respond, a range of different types of associations between muscle and bone will be detected. These may be (1) weak, (2) strong direct, or (3) strong indirect associations (see main text for details).