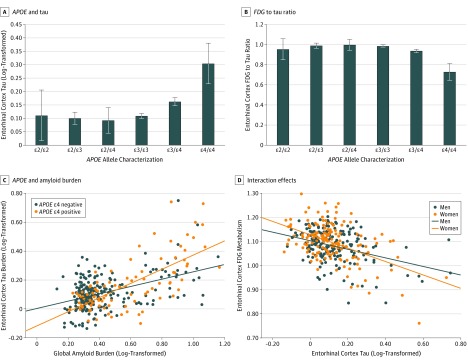
Figure 3. Secondary Analyses of APOE Allele Associations and Interaction Models in the Entorhinal Cortex.
A and B, Compared with individuals who had APOE ɛ3/ɛ3, those with APOE ɛ3/ɛ4 and ɛ4/ɛ4 displayed higher tau deposition (A) and a lower fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) to tau ratio (B) via an analysis of covariance model. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. C, Via interaction studies, in the setting of high global amyloid burden, APOE ɛ4–positive individuals (orange) displayed higher entorhinal cortex tau deposition than their APOE ɛ4–negative counterparts (blue). D, Via interaction studies, in the setting of high entorhinal cortex tau deposition, women (orange) displayed greater tau-mediated metabolic dysfunction than men (blue).