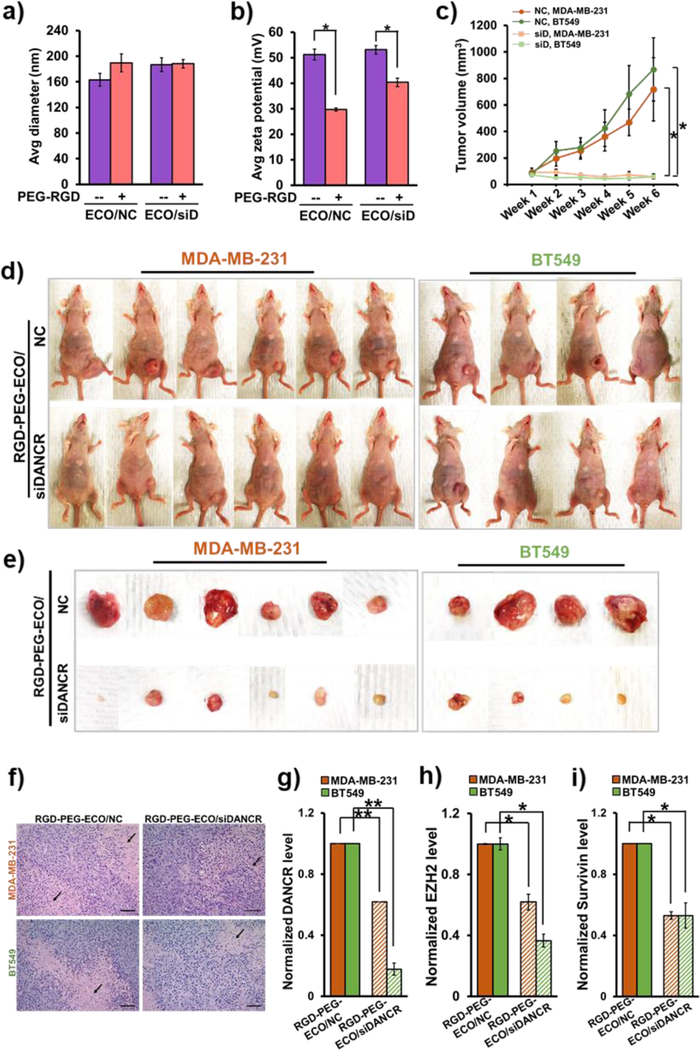
Figure 6.
Systemic therapy of RGD-PEG-ECO/siDANCR nanoparticles significantly reduces primary tumor burden in TNBC xenografts. RGD-PEG-ECO/NC and RGD-PEG-ECO/siDANCR nanoparticles were formulated at N/P = 8, PEG-RGD/ECO = 2.5 mol% and [siRNA] = 0.3 mg/mL, and characterized for (a) particle size and (b) zeta potential (*p<0.05). (c) Weekly intravenous injections of RGD-PEG-ECO/siDANCR nanoparticles at a siRNA dose of 1.0 mg/kg for 6 weeks result in significant reduction in tumor volumes (*p<0.05). MDA-MB-231 and BT549 xenografts (2 & 4 × 106 cells, respectively) were implanted into the mammary fat pads of athymic mice and treatment was started at average tumor volume of 70–90 mm3. (d) Compared to RGD-PEG-ECO/NC, RGD-PEG-ECO/siDANCR nanoparticles mediate significant inhibition of tumor progression. (e) Tumor status at the end of 6 weeks. (f) H&E staining of paraffin-fixed tumor samples from mice treated with RGD-PEG-ECO/siDANCR and NC (scale bar = 100 μm) shows large zonal necrosis (arrows) in NC but only focal necrosis with siDANCR treatment. Compared to RGD-PEG-ECO/NC-treated tumors, RGD-PEG-ECO/siDANCR-treated tumors demonstrate (g) significantly reduced DANCR levels (**p<0.005), and significantly lower mRNA expression of (h) EZH2 and (i) survivin, indicating that the targeted RGD-PEG-ECO-siDANCR therapy likely causes epigenetic alterations and apoptosis in the TNBC tumors (*p<0.05).